Image Analysis: Making the Most of Your Time at the Shore
Anonym
If hand digitizing geographic features is the bane of a GIS technician's existence, tasking someone to manually delineate ephemeral features of say, the banks of the Mississippi River, is downright inhumane. But someone has to do it; maintaining accurate extents of water bodies is critical for those responsible for maritime transportation operations, ecological research, and flood assessments. If the trend of global climate change continues, the need to analyze shorelines and update feature databases will grow. Could this eventuality presage untold hours of servitude behind digitizing tablets? Thankfully, the pace of geospatial innovation and interoperability between GIS and remote sensing technology offers another, more efficient, option for meeting this challenge.
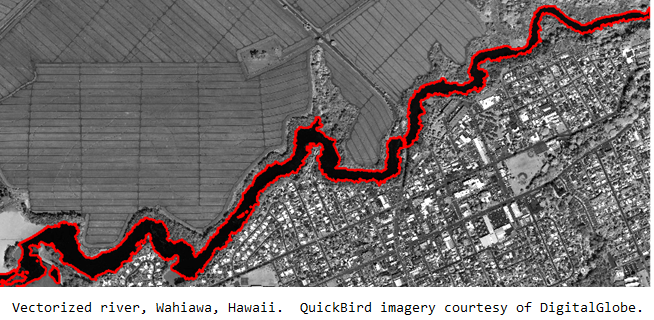
If one were to reflect on past trends in geospatial mapping techniques, the availability of higher resolution imagery from remote sensing platforms marks a sea change among those in the GIS community. Once imagery was recognized as a new source for accurate and timely geographic information rather than simply a basic contextual map backdrop, users began to identify and trace features of interest directly onscreen—making the traditional method of hand-digitizing water features from existing paper maps for inclusion in electronic spatial analysis models seem archaic. However, the heads-up digitization of features like rivers and shorelines is still very tedious and time consuming; the highly manual process entails many mouse clicks and a skilled GIS technician with a steady hand. Manual efforts are expensive in terms of time and money, which prove to be a budgetary challenge for projects that require ongoing updates and analysis, like coastal mapping. A more efficient method for extracting coastline information from image data is required.
Over several decades, image processing algorithms have been refined to interpret the spatial, spectral, and textural characteristics of data contained within a pixel and its relationships to neighboring pixels. Since these remote sensing techniques yield features of interest represented by vectorized spatial objects, they are highly interoperable with GIS analysis workflows. Moreover, these feature extraction algorithms can be automated to comb through large amounts of geospatial data—making the delineation of coastline features an ideal application. The rapid production of this geographic information is invaluable for updating existing maps or feeding decision support systems that address critical questions relating to land-water interfaces.
The prospects for more timely and efficient methods to map changing coastlines are bright. Today, remote sensing platforms allow us to repeatedly capture information over vast coastal areas that are too costly or dangerous to access from the ground. Soon, we will witness an explosion of new image data produced by an increasing number of remote sensing platforms such as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) and small scale satellites. With a burgeoning image archive accessible via published image service, and the ability to utilize automated coastline feature extraction routines to conduct ongoing and historical analysis, the only uncertainty is this: What will you do with the time previously allocated to hand digitizing shoreline?