The ENVI Deep Learning module is a solution to this challenge. Deep learning is a form of Artificial Intelligence that enables the user to ‘teach’ the software how to recognize nearly any feature or condition in the data from spatial, spectral or other characteristics. Whereas Machine Learning algorithms require a user to ‘show’ the computer hundreds of examples of the feature to be identified, Deep Learning uses iterative algorithms that can learn from just a dozen examples in some cases. “As with our other modules, you don’t have to be an Artificial Intelligence expert to use the ENVI Deep Learning module,” said Griebel. “The module has intuitive tools and workflows that enable users to easily label data and generate models with the click of a button.”
For more seasoned imagery experts, the module gives the option of fusing information layers from different remote sensing data sets to create more robust object classifiers. Griebel explained that environmental consultants have embraced the ENVI Deep Learning module for the significant savings in time it provides them, compared with manual processes. One early adopter has taught the module to find and count certain species of wildlife – as small as geese – in high-resolution satellite imagery to determine if the population is increasing or decreasing over time.
This task is incredibly time consuming using manual methods because the animals may number in the thousands, and they are never in the exact same locations from one image collection to another. Once trained, the algorithms evaluate the imagery covering a given study area in a matter of seconds. More importantly, the same Deep Learning algorithm can be applied repeatedly with new images as they are collected.
The time savings of Deep Learning is an obvious benefit, but Griebel said this Artificial Intelligence technique is having another dramatic impact on environmental consultants and other NV5 clients. The ability to identify and map objects and features has become so refined that users are expanding their applications of remotely sensed data to analyze geographic areas that are much larger than they would have ever considered with manual methods in the past. “They can extract features on a much bigger scale now,” he said.
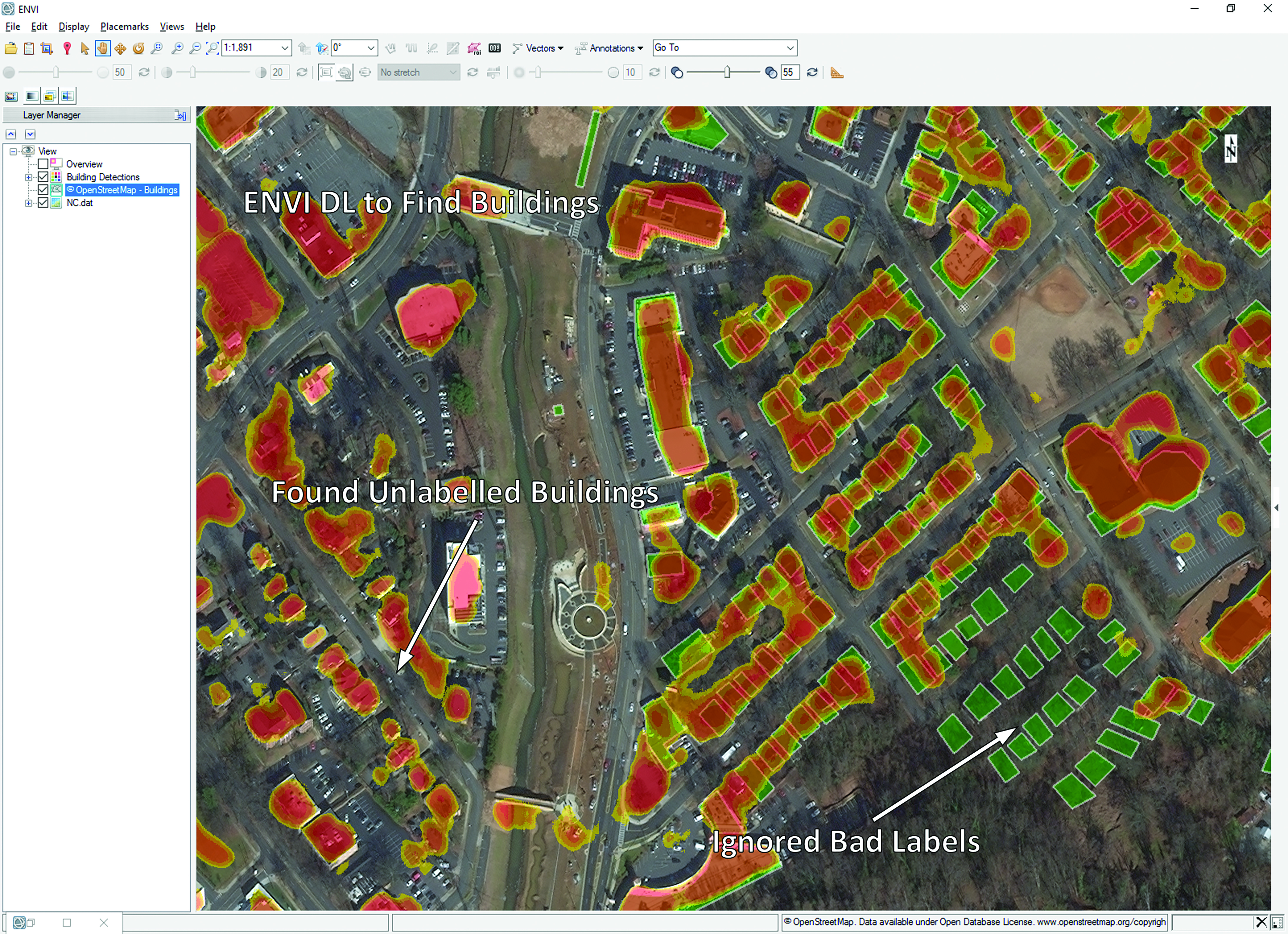
Using ENVI’s proven analytics, additional data layers for deep learning can be created to accentuate features of interest. These data layers aid in the development of more robust and accurate classifiers by helping neural networks more easily learn where they need to focus.