ENVI Advances GPU-Enabled Geospatial Processing
Anonym
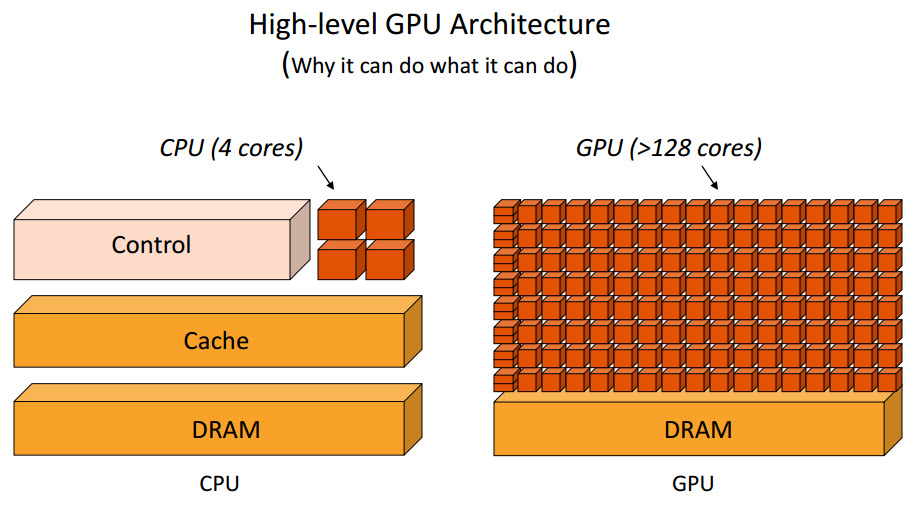
We've recently been working with our partner NVIDIA® to improve the performance of some of our most-used geospatial analysis algorithms by leveraging the power of their Graphic Processing Units, or GPUs. GPUs are specialized computer processors that are designed to improve graphical analysis and performance by supporting multiple parallel processes at the same time. This is especially useful when conducting large raster analysis as it increases the amount of data that can analyzed simultaneously, vastly decreasing processing time.

What we've done is leveraged NVIDIA's CUDA parallel computing platform and programming model to build GPU enabled geospatial algorithms. These algorithms significantly shorten the amount of time it takes to run them by taking advantage of the parallel processing capabilities of NVIDIA GPUs. Potential users of this technology could be organizations building high volume, on-demand geospatial analysis platforms. GPU accelerated algorithms would reduce the time it would take to run on-demand geospatial analytics, resulting in faster results and less drain on the system overall.
Another potential user is the one that has a ton of data that they need to analyze on a regular basis. The time savings realized through the use of these algorithms is compounded over multiple datasets, and programmatic access to the functionality means that significant improvements in workflow can be created by reducing processing time, as well as the resources needed to manually run those processes.
After running some preliminary tests on these algorithms, we saw improvements of eight to forty times over running the same analysis on a standard CPU. At these rates, even a single desktop user can realize significant time savings when performing analysis on large datasets or multiple images.
ENVI GPU-Enabled Algorithms
Below is a list of four algorithms we've GPU enabled thus far. These are available as an ENVI plug-in for desktop use, a task for ENVI Services Engine, or for programmatic access.
High Speed Orthorectification:
High-SpeedOrtho (HSO) optimizes orthorectification image processing using the powerful processing capabilities available on modern graphics cards, resulting in dramatic improvements in execution speed. ENVI's orthorectification tools allow you to orthorectify images using rational polynomial coefficients (RPCs), elevation and geoid information, and optional ground control points (GCPs). RPCs attempt to model the sensor geometry, using a polynomial approximation to model light rays from a ground location to the focal plane of the sensor. However, RPCs and elevation information do not provide enough details to build a rigorous model representing the path of light rays from a ground object to the sensor.
Atmospheric Correction
High-SpeedQuick Atmospheric Correction (HSQUAC) optimizes QUAC®, the popular and easy-to-use atmospheric correction tool for remote sensing imagery. QUAC is an atmospheric correction method for multispectral and hyperspectral imagery that works with the visible and near-infrared through shortwave infrared (VNIR - SWIR) wavelength range.
Principal Components
High-Speed PCA (HSPCA) optimizes a commonly used data transform employed across virtually all disciplines, Principal Components Analysis (PCA). PCA is used to produce uncorrelated output bands, to segregate noise components, and to reduce the dimensionality of data sets. Because multispectral data bands are often highly correlated, the principal components (PC) transformation is used to produce uncorrelated output bands. This is done by finding a new set of orthogonal axes that have their origin at the data mean and that are rotated so the data variance is maximized.
Adaptive Coherence Estimator
High-Speed ACE (HSACE) optimizes the popular spectral target detection method, Adaptive Coherence Estimator (ACE). ACE is derived from the Generalized Likelihood Ratio (GLR) approach. The ACE is invariant to relative scaling of input spectra and has a Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) with respect to such scaling. Similar to Constrained Energy Minimization (CEM) and Matched Filtering (MF), ACE does not require knowledge of all the endmembers within an image scene. Computing an ACE result can often be time consuming, especially for large images. The HSACE technology dramatically improves processing speeds using the power of modern graphics cards.
We're very excited to see the work we've put into our GPU enabled geospatial algorithms paying off in terms of significant time savings for our customers, and are even more excited to be working with NVIDIA, one of the foremost producers of GPUs in the world today. Together our goal is to push the field of geospatial processing by combining best-in-class hardware with superior software algorithms to take advantage of new advances in computing technologies. For more information on our new GPU enabled algorithms feel free to contact us, and keep your eyes out for some upcoming webinars and whitepapers surrounding this exciting new technology!