User Interface Elements
When writing a custom task, you can choose to display a dialog that lets the end user select input and output parameters for ENVITasks. This topic describes various user interface (UI) elements that you can add to dialogs.
In a style sheet, set the type key to one of these UI elements. For example:
"parameters": [
{
"name": "raster_filename",
"type": "IDLLabel_UI"
}
Some elements have keywords that let you display specific options for the end user to choose. These are described in each section below. For example:
"name": "raster_filename",
"type": "IDLList_UI",
"keywords": {
"OPTIONS": ['Band 1', 'Band 2', 'Band 3', 'Band 4']
}
Or:
"name": "raster_filename",
"type": "ENVIRaster_UI",
"keywords": "MULTIPLE"
To see a preview of a UI element, pass it to the ENVIUI::CreateFromDialog method. You can also set keywords on some elements, as this example shows:
e = ENVI()
UI = e.UI
element = IDLList_UI(OPTIONS=['Band 1', 'Band 2', 'Band 3', 'Band 4'])
result = UI.CreateFromDialog(element)
ENVI Elements
The following UI elements are unique to the ENVI interface. They are listed in alphabetical order.
|
Type
|
ENVIColorMap_UI
|
|
Description
|
Choose a color table.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
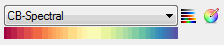
|
|
Return Value
|
A color table, for example:
BLUE = 66, 67, 67, 68, 68, ...
GREEN = 1, 3, 6, 8, 11, ...
PALETTE = 158, 1, 66, 160, 3, ...
RED = 158, 160, 162, 165, 167, ...
|
|
Type
|
ENVIColorMapName_UI
|
|
Description
|
Set a color table name.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
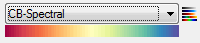
|
|
Return Value
|
A color table name, for example:
CB-Spectral |
|
Type
|
ENVIColorTable_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select a predefined or custom color table.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A 256 x 3 array of RGB values that define the color table
|
|
Type
|
ENVICoordSys_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter parameters for a coordinate system. You can use the coordinate system from an existing dataset or from the current view. Or, click the  button to display the Select Coordinate System dialog. button to display the Select Coordinate System dialog.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
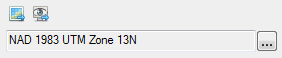
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVICoordSys object, for example:
ENVICOORDSYS <253938>
COORD_SYS_CODE = 0
COORD_SYS_STR = 'PROJCS["NAD_1983_UTM_Zone_13N",
GEOGCS["GCS_North_American_1983",
DATUM["D_ North_American_1983",
SPHEROID["GRS_1980",6378137.0,298.257222101]],
PRIMEM ["Greenwich",0.0],
UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]],
PROJECTION["Transverse_Mercator"],
PARAMETER["False_Easting",500000.0],
PARAMETER["False_Northing",0.0],
PARAMETER["Central_Meridian",-105.0],
PARAMETER["Scale_Factor",0.9996],
PARAMETER["Latitude_Of_Origin",0.0],
UNIT["Meter",1.0]]'
|
|
Type
|
ENVICoordSysString_UI
|
|
Description
|
This is similar to ENVICoordSys_UI but is meant for capturing a coordinate system string.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A coordinate system string, for example:
PROJCS["NAD_1983_UTM_Zone_13N",
GEOGCS["GCS_North_American_1983",
DATUM["D_North_American_1983",
SPHEROID["GRS_1980",6378137.0,298.257222101]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0],
UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]],
PROJECTION["Transverse_Mercator"],
PARAMETER["False_Easting",500000.0],
PARAMETER["False_Northing",0.0],
PARAMETER["Central_Meridian",-105.0],
PARAMETER["Scale_Factor",0.9996],
PARAMETER["Latitude_Of_Origin",0.0],
UNIT["Meter",1.0]]
|
|
Type
|
ENVIFeatureCount_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select an ENVI Feature Counting file.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
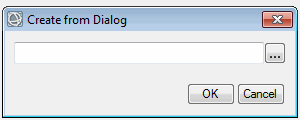
Use this dialog to select an ENVI Feature Counting file (.efc).
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIFeatureCount object that contains the URI to the .efc file; for example:
ENVIFEATURECOUNT <285284>
URI: C:\MyData\Buildings.efc
|
|
Type
|
ENVIGCPSet_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select an ENVI Ground Control Point (GCP) file.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

Use this dialog to select an ENVI GCP file (.pts).
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIGCPSet object, for example:
ENVIGCPSET <297131>
COORD_SYS_CODE = 32612
COORD_SYS_STR = 'PROJCS["WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_12N",GEOGCS["GCS_WGS_1984",DATUM["D_WGS_1984",SPHEROID["WGS_1984",6378137.0,298.257223563]],PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0],UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]],PROJECTION["Transverse_Mercator"],PARAMETER["False_Easting",500000.0],PARAMETER["False_Northing",0.0],PARAMETER["Central_Meridian",-111.0],PARAMETER["Scale_Factor",0.9996],PARAMETER["Latitude_Of_Origin",0.0],UNIT["Meter",1.0]]'
Total GCPs: 14
0: {408620.650000 3698081.000000 314.977000 4365.000000 446.000000 }
1: {406652.050000 3698011.500000 311.083000 3568.000000 478.000000 }
etc... |
|
Type
|
ENVIGridDefinition_UI
|
|
Description
|
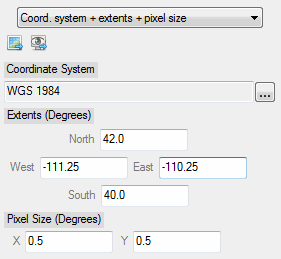
Create a grid definition.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIGridDefinition object, for example:
ENVIGRIDDEFINITION <256169>
EXTENTS = -111.25000, 42.000000, -110.25000, 40.000000
NCOLUMNS = 2
NROWS = 4
SPATIALREF = <ObjHeapVar256172 (ENVISTANDARDRASTERSPATIALREF)>
|
|
Type
|
ENVIPointCloud_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select a LAS-format point cloud file.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

Use this dialog to select a point cloud file in LAS format.
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIPointCloud object, for example:
ENVIPOINTCLOUD <264406>
DATA_RANGE = 593741.00, 5289518.0, 334.01000...
DIRECT_READ = 0
NPOINTS = 6459297
... |
|
Type
|
ENVIPointCloudSpatialRef_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter parameters for a spatial reference object that applies to ENVI point clouds.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
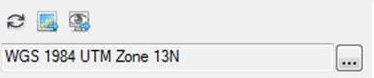
Use this dialog to select a point cloud spatial reference.
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIPointCloudSpatialRef object
|
|
Type
|
ENVIPseudoRasterSpatialRef_UI
|
|
Description
|
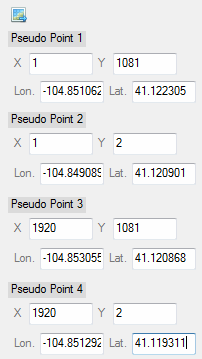
Enter parameters for a pseudo spatial reference.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIPseudoRasterSpatialRef object, for example:
ENVIPSEUDORASTERSPATIALREF <257560>
COORD_SYS_CODE = 0
COORD_SYS_STR = 'GEOGCS["GCS_WGS_1984",
DATUM["D_WGS_1984",
SPHEROID["WGS_ 1984",6378137.0,298.257223563]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0],
UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]]'
PSEUDO_GEO_POINT_1 = 1.0000000, 1081.0000, -104.85106, 41.122305
PSEUDO_GEO_POINT_2 = 1.0000000, 2.0000000, -104.84909, 41.120901
PSEUDO_GEO_POINT_3 = 1920.0000, 1081.0000, -104.85306, 41.120868
PSEUDO_GEO_POINT_4 = 1920.0000, 2.0000000, -104.85129, 41.119311
|
|
Type
|
ENVIRaster_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select an image that is in ENVI raster format.
|
|
Keywords
|
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to allow the user to select more than one raster.
DISABLE_SUB_RECT: Set this keyword to disable spatial subsetting from the Data Selection dialog.
DISABLE_BANDS: Set this keyword to disable spectral subsetting from the Data Selection dialog.
DISABLE_MASK: Set this keyword to disable selecting an input mask from the Data Selection dialog.
|
|
Example
|
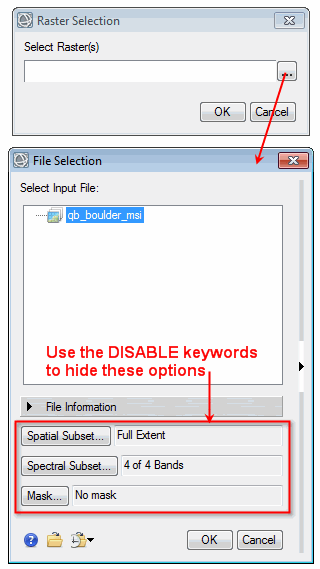
Example with MULTIPLE keyword set:
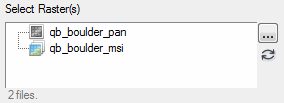
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIRaster object or array of ENVIRaster objects, for example:
ENVIRASTER <349142>
AUXILIARY_SPATIALREF = !NULL
AUXILIARY_URI = <Array[2]>
DATA_TYPE = 'uint'
etc.
|
|
Type
|
ENVIROI_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select one or more regions of interest (ROIs) that have already been opened in ENVI.
|
|
Keywords
|
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to allow the user to select more than one ROI.
|
|
Example
|
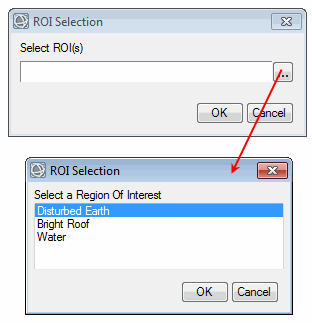
Example with MULTIPLE keyword set:
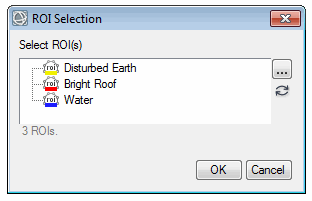
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIROI object or array of ENVIROI objects, for example:
<ObjHeapVar379877(ENVIROI)>
|
|
Type
|
ENVIRPCRasterSpatialRef_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter parameters for an RPC spatial reference.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
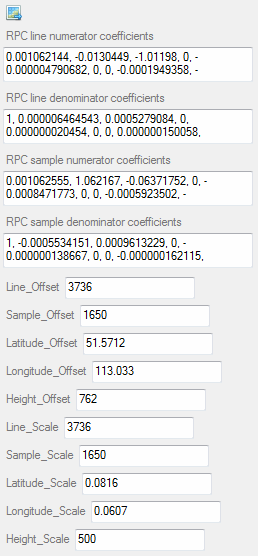
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIRPCRasterSpatialRef object, for example:
ENVIRPCRASTERSPATIALREF <437975>
COORD_SYS_CODE = 0
COORD_SYS_STR = 'GEOGCS["GCS_WGS_1984",
DATUM["D_WGS_1984",
SPHEROID["WGS_1984",6378137.0,298.257223563]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0],
UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]]'
RPC_LINE_DEN_COEFF = 1.0000000, 6.4645428e-006, 0.00052790839, 0.00000000, ...
RPC_LINE_NUM_COEFF = 0.0010621439, -0.013044900, -1.0119801, 0.00000000, ...
RPC_OFFSETS = 3736.0000, 1650.0000, 51.571200, 113.03300, 762.00000
RPC_SAMP_DEN_COEFF = 1.0000000, -0.00055341510, 0.00096132292, 0.00000000, ...
RPC_SAMP_NUM_COEFF = 0.0010625550, 1.0621670, -0.063717522, 0.00000000, ...
RPC_SCALES = 3736.0000, 1650.0000, 0.081600000, 0.060700000, 500.00000
|
|
Type
|
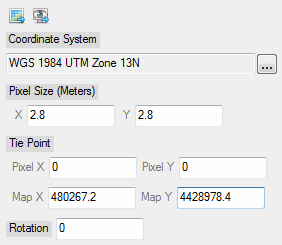
ENVIStandardRasterSpatialRef_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter parameters for a standard spatial reference.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIStandardRasterSpatialRef object, for example:
ENVISTANDARDRASTERSPATIALREF <381116>
COORD_SYS_CODE = 0
COORD_SYS_STR = 'PROJCS["UTM_Zone_13N",
GEOGCS["GCS_WGS_1984",
DATUM["D_WGS_1984",
SPHEROID["WGS_1984",6378137.0,298.257223563]],
PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0],
UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]],
PROJECTION["Transverse_Mercator"],
PARAMETER["False_Easting",500000.0],
PARAMETER["False_Northing",0.0],
PARAMETER["Central_Meridian",-105.0],
PARAMETER["Scale_Factor",0.9996],
PARAMETER["Latitude_Of_Origin",0.0],
UNIT["Meter",1.0]]'
PIXEL_SIZE = 2.8000000, 2.8000000
ROTATION = 0.00000000
TIE_POINT_MAP = 480267.20, 4428978.4
TIE_POINT_PIXEL = 0.00000000, 0.00000000
|
|
Type
|
ENVITiePointSet_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select an ENVI tie point file. The header in this file must reference the locations of two input rasters.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

Use this dialog to select an ENVI tie point file (.pts).
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVITiePointSet object, for example:
URI = C:\MyData\SampleTiePoints.pts
INPUT_RASTER1 = <ObjHeapVar332386(ENVIRASTER)>
INPUT_RASTER2 = <ObjHeapVar333409(ENVIRASTER)>
Total Tie Points: 104
0: { 229.994797 1078.083374 502.200623 817.015991 }
1: { 939.005188 283.916656 932.200623 326.640991 }
etc... |
|
Type
|
ENVITime_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter the acquisition date and time for a dataset.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVITime object, for example:
ENVITIME <437990>
ACQUISITION = '2016-08-04T12:18:23Z'
UNIX_MILLISECONDS = 1470313103000
UNIX_SECONDS = 1470313103
|
|
Type
|
ENVITimeString_UI
|
|
Description
|
This is similar to ENVITime_UI but is meant for capturing an acquisition time string.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
An acquisition time string, for example:
2016-08-04T12:20:09Z
|
|
Type
|
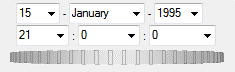
ENVITimeWheel_UI
|
|
Description
|
This is similar to ENVITime_UI but has a wheel control to reduce the number of clicks.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVITime object, for example:
ENVITIME <444818>
ACQUISITION = '1995-01-15T21:00:00Z'
UNIX_MILLISECONDS = 790203600000
UNIX_SECONDS = 790203600
|
|
Type
|
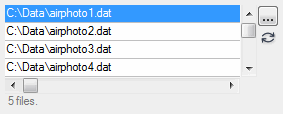
ENVIURI_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select a file and record its uniform resource indicator (URI). The URI contains the full path and filename for the selected file.
|
|
Keywords
|
FILTER: Set this keyword to allow filtering of file types.
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to allow the user to select more than one file.
|
|
Example
|

Example with MULTIPLE keyword set:
|
|
Return Value |
A URI string or an array of URI strings, for example:
C:\Data\envi.json
|
|
Type
|
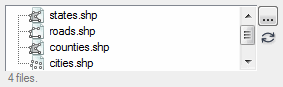
ENVIVector_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select a supported vector file.
|
|
Keywords
|
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to allow the user to select more than one vector file.
|
|
Example
|

Example with the MULTIPLE keyword set:
|
|
Return Value
|
An ENVIVector object or array of ENVIVector objects, for example:
ENVIVECTOR <568229>
AUXILIARY_URI = <Array[6]>
COORD_SYS = <ObjHeapVar568250(ENVICOORDSYS)>
DATA_RANGE = -158.17646, 19.702482, -68.783012, 64.848302
RECORD_TYPE = 'Point'
URI = 'INSTALL_DIR\ENVIxx\classic\data\vector\cities.shp'
|
IDL Elements
The following are generic UI elements that map to other IDL variable types.
|
Type
|
IDLAddRemoveList_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select any number of strings from a list.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
|
|
Example
|
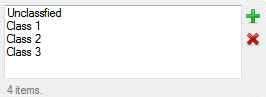
|
|
Return Value
|
A string array of items in the list, for example:
Unclassified
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3 |
|
Type
|
IDLAddRemoveReorderList_UI
|
|
Description
|
This is similar to AddRemoveList_UI but also lets the user reorder selected items.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
|
|
Example
|
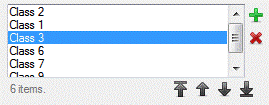
|
|
Return Value
|
A string array of items in the list, for example:
Unclassified
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3 |
|
Type
|
IDLBool_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select to perform an action or not.
|
|
Keywords
|
LABEL_0: Set this keyword to a string label for the first option.
LABEL_1: Set this keyword to a string label for the second option.
|
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value |
Returns a Boolean value of true or false.
|
|
Type
|
IDLBoundingBox_UI
|
|
Description
|
Define a bounding box using latitude/longitude coordinates.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
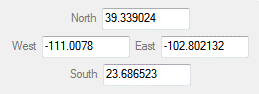
|
|
Return Value
|
A double-precision, four-element array of coordinates, for example:
-111.0078 23.686523 -102.802132 39.339024
|
|
Type
|
IDLCheckBoxes_UI
|
|
Description
|
Create a set of buttons for the user to choose from. The buttons are non-exclusive (multiple items can be selected).
|
|
Keywords
|
COLUMN: Set this keyword to true to arrange the buttons in a column (vertically). The default is horizontal arrangement.
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to an array with the options to display.
|
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
An array with the selected items.
|
|
Type
|
IDLColorEditTree_UI
|
|
Description
|
Edit the colors of pre-defined classes.
|
|
Keywords
|
Option 1: Set the OPTIONS keyword to strings with class names, and set the VALUE keyword to RGB color triplet values.
Option 2 (shown below): Set the VALUE keyword to a hash with class names for the keys and RGB color triplets for the values.
|
|
Example
|
a = ORDEREDHASH( $
'Unclassified', [0b, 0, 0], $
'Class 1', [255b, 0, 0], $
'Class 2', [0b, 255, 0], $
'Class 3', [0b, 0, 255])
result = UI.CreateFromDialog(IDLColorEditTree_UI(value=a))
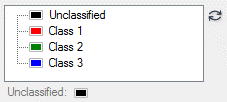
|
|
Return Value
|
A (3, n) byte array with RGB color triplets of each class, for example:
0 0 0
255 0 0
0 255 0
0 0 255
|
|
Type
|
IDLColor_UI
|
|
Description
|
Choose a standard or custom color.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
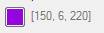
|
|
Return Value
|
A three-element byte array that represents an RBB color triplet, for example:
150 6 220
|
|
Type
|
IDLColorTableName_UI
|
|
Description
|
Choose a color table using radio buttons.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A string with the name of a color table, for example:
Blue-Red |
|
Type
|
IDLComplexNumber_UI or IDLDoubleComplexNumber_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter a complex or double-complex number (with real and imaginary components).
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A complex or double-complex array with real and imaginary components, for example:
( -1.5000000, 3.5000000)
|
|
Type
|
IDLContainer_UI
|
|
Description
|
This is a container that holds multiple UI classes so that they can be displayed at once (for example, in a workflow).
|
|
Keywords
|
CAN_TOGGLE: Set this keyword to display a check box that lets users choose to show or hide groups of smaller UI classes. See IDLContainer_UI Examples.
COLUMN: Set this keyword to place all UI classes in one column.
FRAME: Set this keyword to put a frame around the container.
ROW: Set this keyword to place all UI classes in one row.
TOGGLE_LABEL: Set this keyword to a string with a label for a group of UI classes, when the CAN_TOGGLE keyword is set. The default value is "Show Parameters."
|
|
Example
|
See IDLContainer_UI Examples. Also see the workflow examples in Custom User Interface Classes.
|
|
Return Value
|
An instance of the IDLContainer_UI class:
{
"raster": "<ObjHeapVar240325(ENVIRASTER_UI)>",
"vector": "<ObjHeapVar240337(ENVIVECTOR_UI)>"
} |
|
Type
|
IDLDropList_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select an option from a drop-down list.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
|
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A string with the selected value, for example:
Water |
|
Type
|
IDLEditableDropList_UI
|
|
Description
|
Select an option from a drop-down list, or enter a different option by typing it.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
REMEMBER_VALUES_ID: Set this keyword to a string with a unique identifier for saving previous values selected by the user (up to a maximum of 15). These values will populate the drop-down list the next time this UI class is used, as long as it is created with the same string in the REMEMBER_VALUES_ID keyword.
|
|
Example
|
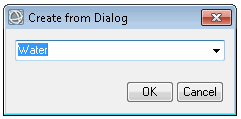
|
|
Return Value |
A string with the selected value, for example:
Water |
|
Type
|
IDLEditableList_UI
|
|
Description
|
Edit the items in a list.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
|
|
Example
|
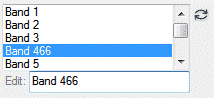
|
|
Return Value
|
A string array with the updated list, for example:
Band 1
Band 2
Band 3
Band 466
Band 5 |
|
Type
|
IDLHidden_UI
|
|
Description
|
Use this class to hide parameters in a custom task.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
PARAMETER |
|
Return Value
|
A value of hidden in the task file
|
|
Type
|
IDLKernel_UI
|
|
Description
|
Define a kernel array for filtering operations.
|
|
Keywords
|
TYPE: Specify an IDL numeric data type: byte, int, long, float, double, complex, dcomplex, uint, ulong, long64, ulong64.
|
|
Example
|
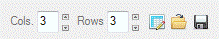
|
|
Return Value
|
An array [columns, rows] representing the kernel, for example:
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
|
|
Type
|
IDLLabel_UI
|
|
Description
|
Use this with custom tasks only. Enter a text label that cannot be edited. For example, display the name of an input raster that the user cannot change.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
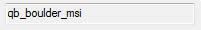
|
|
Return Value
|
The text label, for example:
qb_boulder_msi |
|
Type
|
IDLList_UI
|
|
Description
|
Create a list of options for a user to select, either individually or more than one using the Ctrl or Shift key.
|
|
Keywords
|
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to true to allow selection of more than one element in the list. This is the default behavior.
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
|
|
Example
|
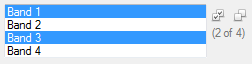
|
|
Return Value
|
A string array with the selected items, for example:
Band 1
Band 3 |
|
Type
|
IDLMultiString_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter multiple strings.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
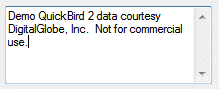
|
|
Return Value
|
A string array, for example:
Demo QuickBird 2 data courtesy
DigitalGlobe, Inc. Not for commerical
use. |
|
Type
|
IDLNumeric_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter a numeric value.
|
|
Keywords
|
TYPE: Specify an IDL numeric data type: byte, int, long, float, double, complex, dcomplex, uint, ulong, long64, ulong64.
|
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
The numeric value, for example:
10.002000 |
|
Type
|
IDLNumericColsRows_UI
|
|
Description
|
Define the number of columns and rows for a raster.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A two-element integer array, for example:
123 234 |
|
Type
|
IDLNumericPair_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter a pair of numeric values.
|
|
Keywords
|
TYPE: Specify an IDL numeric data type: byte, int, long, float, double, complex, dcomplex, uint, ulong, long64, ulong64.
LABEL_1: Set this keyword to a string label for the first field.
LABEL_2: Set this keyword to a string label for the second field.
COLUMN: Set this keyword to display the pair in a column. The default is to display them in a row.
|
|
Example
|
pair = numericpair_UI(TYPE='double', LABEL_1='Gain', LABEL_2='Offset', COLUMN=2)

|
|
Return Value
|
A two-element array of numeric values, for example:
0.0010000000000000000 0.00000000000000000
|
|
Type
|
IDLOrderedHash_UI and IDLHash_UI
|
|
Description
|
Create an IDL hash or ordered hash with values that the user can edit.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
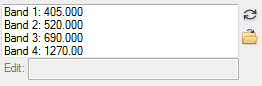
Example
|
Example of an unordered hash:
h = HASH( $
"Band 1", 405.0, $
"Band 2", 520.0, $
"Band 3", 690.0, $
"Band 4", 1273.0)
result = UI.CreateFromDialog(IDLHash_UI(value=h))
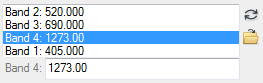
Example of an ordered hash:
h = ORDEREDHASH( $
"Band 1", 405.0, $
"Band 2", 520.0, $
"Band 3", 690.0, $
"Band 4", 1273.0)
result = UI.CreateFromDialog(IDLOrderedHash_UI(value=h))
|
|
Return Value
|
The hash key/value pairs, for example:
{
"Band 1": 405.00000,
"Band 2": 520.00000,
"Band 3": 690.00000,
"Band 4": 1270.0000
} |
|
Type
|
IDLPassword_UI
|
|
Description
|
Display a dialog for entering a password with hidden characters.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
A string with the entered password.
|
|
Type
|
IDLRadioButtons_UI
|
|
Description
|
Create a set of buttons for the user to choose from. The buttons are exclusive (only one item can be selected).
|
|
Keywords
|
COLUMN: Set this keyword to true to arrange the buttons in a column (vertically). The default is horizontal arrangement.
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to an array with the options to display.
|
|
Example
|

|
|
Return Value
|
A scalar with the selected item.
|
|
Type
|
IDLRGBBandSelection_UI
|
|
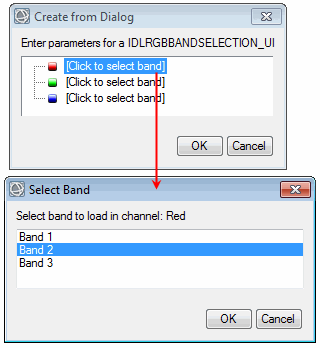
Description
|
Select which bands to assign to red, green, and blue.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array of band names.
|
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
A long array with the selected bands, for example:
2 1 3
|
|
Type
|
IDLRGBGrayScaleBandSelection_UI
|
|
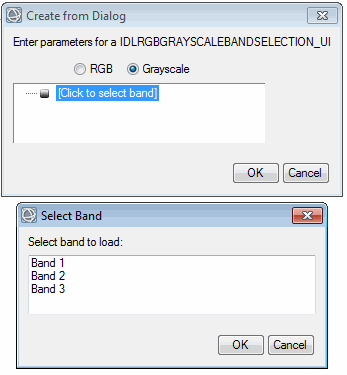
Description
|
Similar to IDLRGBBandSelection_UI but also provides a Grayscale option.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array of band names.
|
|
Example
|
|
|
Return Value
|
An array of the selected bands, for example:
1 |
|
Type
|
IDLSearchList_UI
|
|
Description
|
Create a list of options for a user to select, either individually or more than one using the Ctrl or Shift key. The UI contains a search box to filter the items in the list. This is useful when the list contains a large number of items.
|
|
Keywords
|
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to true to allow selection of more than one element in the list. This is the default behavior.
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the list.
|
|
Example
|
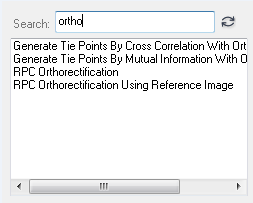
|
|
Return Value
|
A string array with the selected items, for example:
Generate Tie Points By Cross Correlation...
Generate Tie Points By Mutual Information...
RPC Orthorectification
RPC Orthorectification Using Reference Image
|
|
Type
|
IDLSlider_UI
|
|
Description
|
Use a slider to select a numeric value. Set the MAX and MIN properties in the parameter that is associated with this UI element.
|
|
Keywords
|
INCREMENT: Set this keyword to the increment value of the slider.
|
|
Example
|
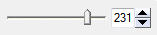
|
|
Return Value
|
A floating-point value, for example:
231.000000 |
|
Type
|
IDLString_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter a text string.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
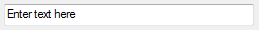
|
|
Return Value
|
A text string, for example:
Enter text here |
|
Type
|
IDLSubRect_UI
|
|
Description
|
Enter X and Y pixel or map coordinates that define a spatial subset.
|
|
Keywords
|
LABEL_X: Set this keyword to a string for the X coordinate label.
LABEL_Y: Set this keyword to a string for the Y coordinate label.
TYPE: Set this keyword to a string with the IDL data type of the coordinates (for example, 'float' or 'int'). The default type is ULong (unsigned integer).
|
|
Example
|
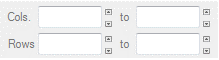
|
|
Return Value
|
A numeric array of coordinate values, for example:
512 512 1024 1024
|
|
Type
|
IDLTree_UI
|
|
Description
|
Create a list of options for a user to select, either individually or more than one using the Ctrl or Shift key.
|
|
Keywords
|
OPTIONS: Set this keyword to a string array with the options to display in the tree.
MULTIPLE: Set this keyword to allow the user to select more than one item in the tree.
|
|
Example
|
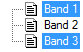
|
|
Return Value
|
A string or string array of the selected items, for example:
Band 1
Band 3 |
|
Type
|
IDLWheel_UI
|
|
Description
|
Use a wheel control to select a numeric value.
|
|
Keywords
|
None |
|
Example
|
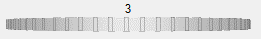
|
|
Return Value
|
A floating-point value, for example:
3.0000000 |