This release includes the following new and improved features.
Highlights
Supported Data Types
Support for the following data formats has been added in this release:
- BlackSky
- Tanager (Planet)
Collaborative File Publishing Using the ENVI Repository
This release introduces the ENVI Repository, which is a cross-platform server that automates the management of file dependencies such as deep learning models, custom tasks with associated code, and spectral libraries across multiple machines. When files are uploaded (published) and then downloaded on different machines, ENVI ensures that all dependencies are downloaded as well and they are placed in a location where they can be found and accessed without conflict.
The following is two workflow examples using the ENVI Repository (example 2 requires an ENVI+IDL installation):

You can publish files using the Share > Publish to Repository option from the ENVI Modeler menu:
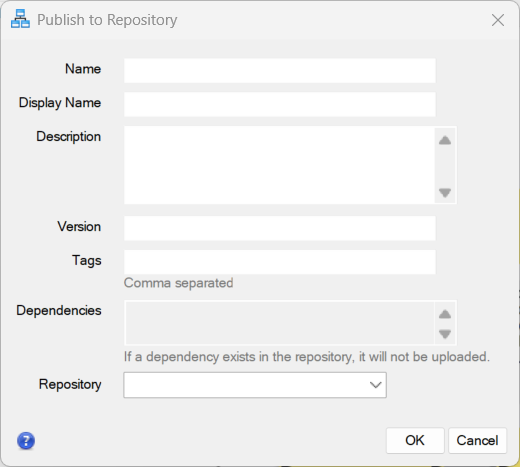
The Share menu in both the ENVI Modeler and the ENVI main menu provides options to download files from a repository server, and to add and manage repository servers. For details, see the ENVI Repository topic.
Spectral Detection and Classification Updates
ENVI's detection and classification algorithms have been refactored, which has improved processing speed by a factor of 2 to 4 times. In addition, covariance regularization options have been added to tasks that require covariance transform, to improve accuracy of spectral detection. Covariance regularization can suppress noise and clutter to improve the signal to noise ratio.
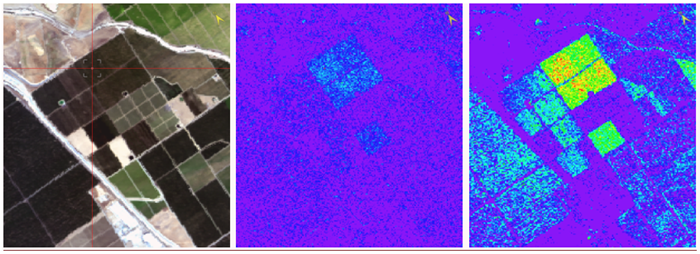
The following images show matched filter detection using image-derived spectra. On the left: Single pixel spectra selection. Center: Matched filter results without covariance regularization. On the right: matched filter results using covariance regularization (truncation). (Both matched filter images are scaled 0-1.)
The refactored tasks are listed below. Those marked with an asterisk (*) include the new covariance regularization parameters. See the New and Updated ENVI Tasks and Routines section at the end of this topic for details on new task parameters.
- ConstrainedEnergyMinimization*
- MahalanobisDistanceClassification*
- MatchedFilter*
- MaximumLikelihoodClassification*
- MinimumDistanceClassification
- MixtureTunedMatchedFilter*
- MixtureTunedTargetConstrainedInterferenceMinimizedFilter
- NormalizedEuclideanDistanceClassification
- OrthogonalSubspaceProjection
- SpectralAdaptiveCoherenceEstimator*
- SpectralAdaptiveCoherenceEstimatorUsingSubspaceBackgroundStatistics*
- SpectralSimilarityMapperClassification
- TargetConstrainedInterferenceMinimizedFilter*
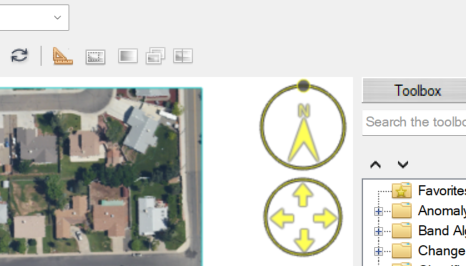
New On-the-Glass Controls
This release includes convenient new Rotate and Fly controls on-the-glass to streamline rotation and navigation within the view. Hover the cursor at the top right corner of the view for the controls to appear. For details on how to use them, see Rotate and Navigation.
Two-Color Multiview Tool
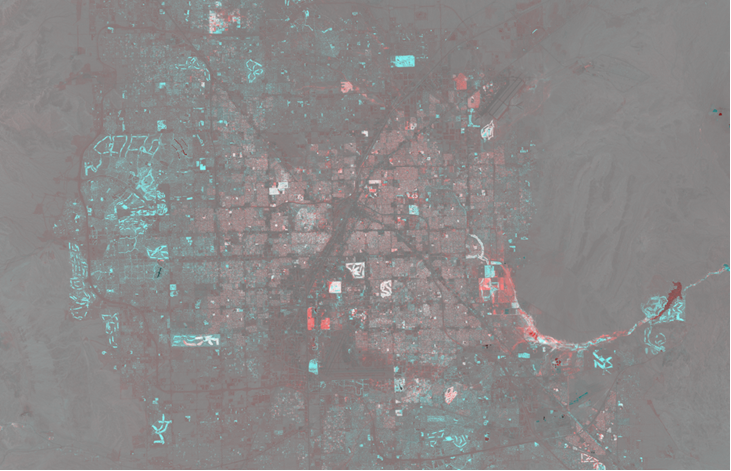
The new Two-Color Multiview tool takes two overlapping single-band rasters and creates a three-band raster product. When the product is combined, the first raster will be applied to the red channel and the second raster will go to the green and blue channels.
If the first raster represents an earlier time, the colors of the output can be interpreted with this mnemonic: red is fled, blue is new. For example, the image below is a two-color multiview composite of NDVI data for Las Vegas from 1985 and 2010. Areas highlighted in blue represent an increase in vegetation index, typically associated with urban expansion. Red areas signify regions where vegetation was lost between the two dates.
Vector Updates
The following vector updates are in this release:
- Vector reading, handling, and visualization performance has improved by up to 10 times for large vector files (such as large vector files from SARscape outputs).
- The 50,000 record limitation for displaying records in the Attribute Viewer has been removed.
- The Virtual Attribute Table Row Threshold setting has been added to the Display General preferences. This setting is applied when viewing attributes for large vector files. When the number of records in the Attribute Viewer table exceeds the setting, the attributes will be displayed in a virtual table to speed up performance.
- A new File > Save As option has been added to save one or more vectors to a GeoJSON file format. See Save Vector As GeoJSON for details.
- Support for empty vectors has been added, to improve how vector data is used with deep learning workflows.
Performance Improvements
The following performance improvements are included in this release:
- Zoom in/out performance is significantly improved.
- Pyramid generation is now 20% faster.
- The Change Detection Workflow has been streamlined to provide significantly faster execution time.
Photogrammetry Module Bundled with ENVI
The Photogrammetry Module is now included in the ENVI installation. Note that a separate license is still required to use the Photogrammetry Module. Contact your sales representative for more information.
ENVITask Template Definition Update
The options parameter key has been introduced in this release. See ENVITask Template Definition for details.
ENVI Server Run Jobs Update
The ENVI Server has the added ability to run jobs in the background without GSF. See Run Jobs in the Background for additional information.
New and Updated ENVI Tasks and Routines
New tasks:
New tasks for the ENVI Repository:
Added object documentation:
- ENVIColorMap: This object contains a color map that can be used when displaying a single raster band to a view. See the updated routines section for routines that have have a COLORMAP property.
New ENVI Repository methods added to the ENVI routine:
- DeleteLocalRepository: Removes the local ENVI Repository folder and files from your machine.
- DownloadFromRepository: Downloads packages from the ENVI Repository to a folder on your machine.
- EditRepositoryPackage: Allows you to edit the details of a package in the ENVI Repository.
- GetLocalPackageInfo: Returns a hash with information related with a package that has been downloaded from the ENVI Repository.
- PingRepository: Verifies if a valid ENVI Repository server is listening and working as expected.
- PublishToRepository: Packages dependencies stored on a local machine and publishes them to the ENVI Repository server.
- RegisterRepository: Adds a connection to an ENVI Repository server.
- UnregisterRepository: Removes an ENVI Repository server registration from the local machine.
Updated tasks:
Updated routines:
The COLORMAP property has been added to the documentation for these routines:
See Also
See What's New (Previous ENVI Releases) for an archive of What's New information.