The MESH_SMOOTH function performs spatial smoothing on a polygon mesh. This function smooths a mesh by applying Laplacian smoothing to each vertex, as described by the following formula:
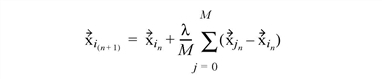
|

|
is vertex i for iteration n
|
| λ
|
is the smoothing factor
|
|
M |
is the number of vertices that share a common edge with xin
|
Syntax
Result = MESH_SMOOTH (Verts, Conn [, ITERATIONS=value] [, FIXED_VERTICES=array] [, /FIXED_EDGE_VERTICES] [, LAMBDA=value])
Return Value
The output of this function is resulting [3, n] array of modified vertices.
Arguments
Verts
Input array of polygonal vertices [3, n].
Conn
Input polygonal mesh connectivity array.
Keywords
ITERATIONS
Number of iterations to smooth. The default value is 50.
FIXED_VERTICES
Set this keyword to an array of vertex indices which are not to be modified by the smoothing.
FIXED_EDGE_VERTICES
Set this keyword to specify that mesh outer edge vertices are not to be modified by the smoothing.
LAMBDA
Smoothing factor. The default value is 0.05.
Examples
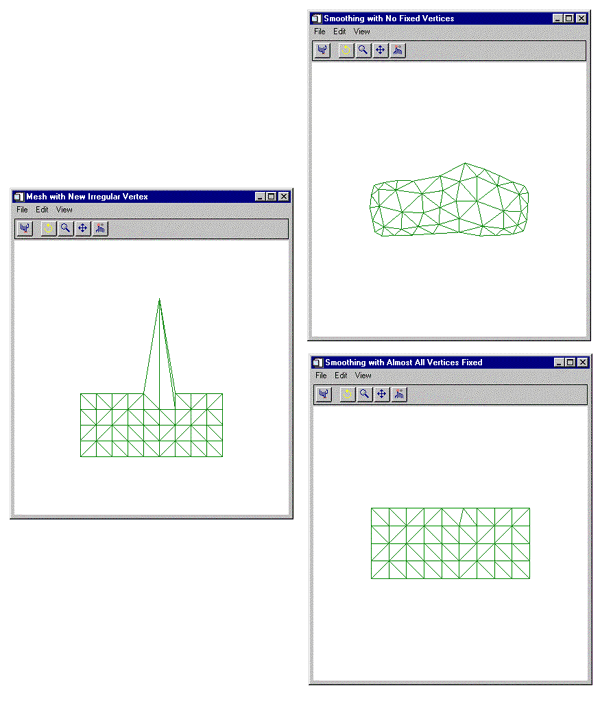
This example smooths a rectangular mesh containing a spike. First, we create a rectangular mesh made up 10 columns and 5 rows of vertices. The vertices are connected with right triangles. The mesh is placed in a polygon object, which is added to a model object. The model is displayed in the XOBJVIEW utility. The XOBJVEW utility allows you to click-and-drag the polygon object to rotate and translate it. See XOBJVIEW for more information on this utility.
When you quit out of the first XOBJVIEW display, the second XOBJVIEW display will appear. The center vertex of the top row is displaced in the y-direction. This displacement causes the center of the top to spike out away from the mesh. After you quit out of the second display, the third display shows the result of smoothing the entire mesh. The final display shows the results of smoothing the spike with all the other vertices fixed.
The example is split into multiple segments; click on each segment to enter the code at the IDL command prompt.
nX = 10
nY = 5
xVertices = FINDGEN(nX) # REPLICATE(1., nY)
PRINT, 'xVertices: '
PRINT, xVertices, FORMAT = '(10F6.1)'
yVertices = REPLICATE(1., nX) # FINDGEN(nY)
PRINT, 'yVertices: '
PRINT, yVertices, FORMAT = '(10F6.1)'
vertices = FLTARR(3, (nX*nY))
vertices[0, *] = xVertices
vertices[1, *] = yVertices
PRINT, 'vertices: '
PRINT, vertices, FORMAT = '(3F6.1)'
TRIANGULATE, xVertices, yVertices, triangles
trianglesSize = SIZE(triangles, /DIMENSIONS)
polygons = LONARR(4, trianglesSize[1])
polygons[0, *] = 3
polygons[1, 0] = triangles
PRINT, 'polygons: '
PRINT, polygons, FORMAT = '(4I6)'
connectivity = REFORM(polygons, N_ELEMENTS(polygons))
oModel = OBJ_NEW('IDLgrModel')
oPolygon = OBJ_NEW('IDLgrPolygon', vertices, $
POLYGONS = connectivity, COLOR = [0, 128, 0], $
STYLE = 1)
oModel->Add, oPolygon
XOBJVIEW, oModel, /BLOCK, $
TITLE = 'Original Mesh'
vertices[1, 45] = 10.
oPolygon->SetProperty, DATA = vertices
XOBJVIEW, oModel, /BLOCK, $
TITLE = 'Mesh with New Irregular Vertex'
smoothedVertices = MESH_SMOOTH(vertices, connectivity)
oPolygon->SetProperty, DATA = smoothedVertices
XOBJVIEW, oModel, /BLOCK, $
TITLE = 'Smoothing with No Fixed Vertices'
fixed = LINDGEN((nX*nY) - 1)
fixed[45] = fixed[45:*] + 1
smoothedVertices = MESH_SMOOTH(vertices, connectivity, $
FIXED_VERTICES = fixed)
oPolygon->SetProperty, DATA = smoothedVertices
XOBJVIEW, oModel, /BLOCK, $
TITLE = 'Smoothing with Almost All Vertices Fixed'
OBJ_DESTROY, [oModel]
The results for this example are shown in the following figure: the spiked mesh (left), and the two smoothed meshes (right).
Version History
See Also
MESH_CLIP, MESH_DECIMATE, MESH_ISSOLID, MESH_MERGE, MESH_NUMTRIANGLES, MESH_OBJ, MESH_SURFACEAREA, MESH_VALIDATE, MESH_VOLUME