The SOBOLSEQUENCE function generates numbers from the Sobol sequence. A Sobol sequence is a low discrepancy quasi-random sequence. Sobol sequences were designed to fill space in a more uniform manner than completely random sampling.
The figures below show the differences between a Sobol sequence and sampling uniformly at random.
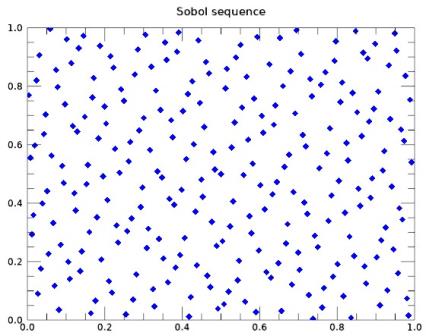
250 points sampled in 2D with a Sobol sequence.
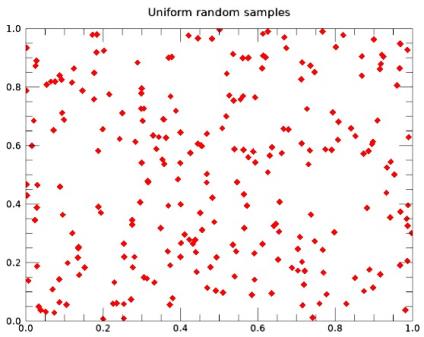
250 points sampled uniformly in 2D at random.
Example
Basic Functionality
print, SobolSequence(2, 4)
IDL prints:
0.50000000 0.50000000
0.25000000 0.75000000
0.75000000 0.25000000
0.37500000 0.62500000
Using STATE
state = 3
print, SobolSequence(state, 2)
IDL prints:
0.50000000 0.50000000 0.50000000
0.25000000 0.75000000 0.25000000
Print the next two sets of values by using STATE:
print, SobolSequence(state, 2)
IDL prints:
0.75000000 0.25000000 0.75000000
0.37500000 0.62500000 0.12500000
Syntax
Result = SOBOLSEQUENCE(STATE [, COUNT])
Return Value
SOBOLSEQUENCE returns an array containing the point(s) in normalized space.
Arguments
STATE
A scalar denoting the number of dimensions to use while initializing the state of the Sobol sequence. This value must be in the range of [1, 6].
If STATE is:
- A constant or expression containing a scalar long integer: The value is used to initialize the state of the Sobol sequence.
- A named variable containing a scalar long integer: The value is used to start a new sequence and the resulting state object is returned in STATE.
- A named variable that contains the state from a previous call: It is used to continue the quasi-random sequence, and the resulting state is returned in STATE.
COUNT
The number of points to return. If omitted, the default is a single n-dimensional point.
Keywords
None.
References
SOBOLSEQUENCE is based on the routine sobseq described in section 7.7 of Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing (Third Edition), published by Cambridge University Press, and is used by permission.
Version History