The SCATTERPLOT3D function displays data as a collection of points, plotted using three-dimensional Cartesian coordinates.
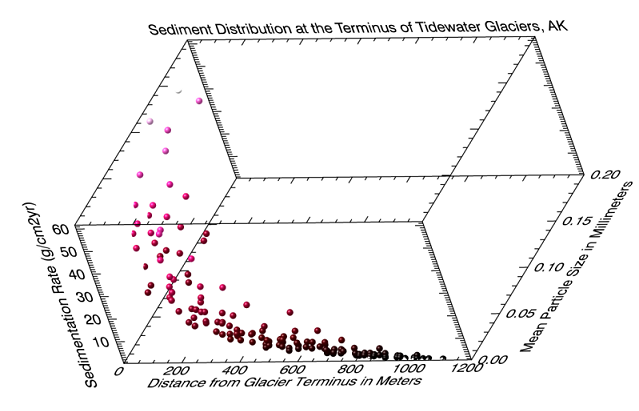
Example
Follow this example to create the plot shown above.
testFile = FILEPATH('ScatterplotData.csv', $
SUBDIRECTORY = ['examples', 'data'])
Navigate to C:\Program Files\***\IDLxx\examples\data and open the file ScatterplotData.csv.
sed_data = READ_CSV(testFile, HEADER=sedHeader, $
N_TABLE_HEADER=1, TABLE_HEADER=sedTableHeader)
PRINT, sedHeader
PRINT, sedTableHeader
dist_size = SCATTERPLOT3D(sed_data.FIELD1, sed_data.FIELD2, $
sed_data.FIELD3, SYM_OBJECT=ORB(), /SYM_FILLED, $
XTITLE='Distance from Glacier Terminus in Meters', $
YTITLE='Mean Particle Size in Millimeters', $
ZTITLE='Sedimentation Rate (g/cm2yr)', $
TITLE='Sediment Distribution at the Terminus of Tidewater Glaciers, AK', $
RGB_TABLE=7, AXIS_STYLE=2, SYM_SIZE=1, MAGNITUDE=sed_data.FIELD3)
IDL displays the field names and the table heading separately:
Distance from Terminus (meters) Mean Particle size (mm) Sedimentation Rate (g/cm2yr)
2012 Simulated Sediment Distribution at the terminus of SE Alaskan Tidewater Glaciers
Click the plot area and use your mouse to rotate the graphic to change its spatial orientation. In the example above, the plot has been rotated to the left and slightly downward. If you rotate the graphic in this way you may need to change the location of the axes to make them more readable. Here is how to switch the text from the left (axis #1) to the right y-axis (axis #4) using the AXES property:
axesList = dist_size.AXES
leftY = axeslist[1]
rightY = axeslist[4]
rightY.TITLE = lefty.TITLE
leftY = ''
rightY.SHOWTEXT = 1
Syntax
graphic = SCATTERPLOT3D(X, Y, Z [, Keywords=value] [, Properties=value])
Keywords
Keywords are applied only during the initial creation of the graphic.
AXIS_STYLE={0|1|2|3}, /BUFFER, /CURRENT, DEPTH_CUE=array, /DEVICE, DIMENSIONS=array, DRAG_QUALITY=quality, LAYOUT=array, LOCATION=array, MARGIN=array, /NODATA, OVERPLOT=1 or variable
Properties
Properties can be set as keywords to the function during creation, or retrieved or changed using the "." notation after creation.
ANTIALIAS, ASPECT_RATIO, AXES, BACKGROUND_COLOR, BACKGROUND_TRANSPARENCY, CLIP, CROSSHAIR, EYE, FONT_COLOR, FONT_NAME, FONT_SIZE, FONT_STYLE, HIDE, MAGNITUDE, MAX_VALUE, MIN_VALUE, NAME, POSITION, RGB_TABLE, SYM_COLOR, SYM_FILLED, SYM_FILL_COLOR, SYM_OBJECT, SYM_SIZE, SYM_THICK, SYM_TRANSPARENCY, SYMBOL, TITLE, UVALUE, WINDOW, WINDOW_TITLE, XRANGE, YRANGE, ZCLIP, ZRANGE
Methods
Close
ConvertCoord
CopyWindow
Delete
Erase
GenerateCode
GetData
GetValueAtLocation
MapForward
MapInverse
Order
Print
Refresh
Rotate
Save
Scale
Select
SetData
Translate
Return Value
The SCATTERPLOT3D function returns a reference to the created graphic. Use the returned reference to manipulate the graphic after creation by changing properties or calling methods.
Arguments
X, Y, Z
Vectors of equal length representing the abscissa (X), ordinate (Y), and applicate (Z) values to be plotted.
Keywords
AXIS_STYLE
Set this keyword to one of the following values:
- 0 - No axes. Decrease the margins so the graphic almost fills the window. This is the default for images.
- 1 - Single X, Y (and Z if 3D) axes located at the minimum data value. The margins will be adjusted to leave space for the axes. This is the default for 3D graphics.
- 2 - Box axes - multiple axes located at both the minimum and maximum data values. The margins will be adjusted to leave space for the axes. This is the default for 2D graphics.
- 3 - Crosshair-style axes - located at the midpoint of each data dimension. Since the axes are in the middle, decrease the margins so the graphic almost fills the window. This is the default for polar plots.
- 4 - No axes, but use the same margins as if axes were there. This is useful if you want to later add another graphic that does have axes, and you want the two visualizations to be aligned properly.
You can set the following properties on the axes:
|
Property |
Description |
|
[XYZ]COLOR |
A string or RGB vector containing the axis color.
|
|
[XYZ]GRIDSTYLE |
A string, integer, or 2-element vector giving the linestyle for tickmarks.
|
|
[XYZ]LOG |
Set to 1 if the axis is logarithmic. The minimum value of the axis range must be greater than zero.
|
|
[XYZ]MAJOR |
The number of major tick marks. Set to -1 to auto-compute, set to 0 to suppress.
|
|
[XYZ]MINOR |
The number of minor tick marks. Set to -1 to auto-compute, set to 0 to suppress.
|
|
[XYZ]SUBGRIDSTYLE
|
A string, integer, or 2-element vector giving the linestyle for the minor tickmarks. The default is 0, for solid lines. Set to -1 to force minor ticks to have the same linestyle as major ticks.
|
|
[XYZ]SHOWTEXT |
Set to 1 to show text labels or 0 to hide the text labels.
|
|
[XYZ]STYLE |
The axis range style. The valid values are:
(0) Nice range. Default for all graphics except Image, Barplot, and Map.
(1) Force the exact data range. Default for Image, Barplot, and Map.
(2) Pad the axes slightly beyond the nice range.
(3) Pad the axes slightly beyond the exact data range.
The [XYZ]RANGE takes precedence over this property.
|
|
[XYZ]SUBTICKLEN |
The ratio of the minor tick length to the major tick length. The default is 0.5.
|
|
[XYZ]TEXT_COLOR |
A string or RGB vector containing the axis text color.
|
|
[XYZ]TEXT_ORIENTATION
|
The angle (in degrees) of the tick mark labels.
|
|
[XYZ]TEXTPOS |
Set to 1 to position text above the axis. The default is 0, below the axis.
|
|
[XYZ]THICK |
Set to a floating-point value between 0 and 10 to specify the line thickness for tickmarks. A thickness of 0 gives a thin hairline. The default is 1.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKDIR |
Set to 1 to draw the tickmarks facing outwards. The default is 0, facing inwards.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKFONT_NAME
|
A string containing the font name for the axis text.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKFONT_SIZE
|
The axis text size in points.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKFONT_STYLE
|
A string or integer containing the font style: normal (0), bold (1), italic (2), or bold italic (3).
|
|
[XYZ]TICKFORMAT |
A string or string array of tick label formats. See Format Codes for more information.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKINTERVAL
|
The interval between major tick marks.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKLAYOUT |
Set to 1 to suppress tick marks; set to 2 to draw a box around the tick labels.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKLEN |
The length of each major tick mark, normalized to the width or height of the graphic. The default value is automatically calculated based upon the aspect ratio of the graphic.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKNAME |
A string array containing the tick labels.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKUNITS |
A string giving the tick units. Valid values are: null (the default, signified by empty quotes), Years, Months, Days, Hours, Minutes, Seconds, Time, exponent for exponential notation, or scientific for scientific notation.
If any of the time units are utilized, then the tick values are interpreted as Julian date/time values. If more than one unit is provided, the axis will be drawn with multiple levels.
|
|
[XYZ]TICKVALUES |
An array of tick mark locations.
|
|
[XYZ]TITLE |
A string giving the axis title.
|
|
[XYZ]TRANSPARENCY
|
An integer from 0-100 giving the percent transparency.
|
For more detailed explanations of these properties, see the AXIS function.
Tip: You can also use the AXIS function to insert additional axes after the graphic has been created.
BUFFER
Set this keyword to 1 to direct the graphics to an off-screen buffer instead of creating a window.
CURRENT
Set this keyword to create the graphic in the current window. If no window exists, a new window is created. The WINDOW's SetCurrent method may be used to set the current window.
Or, set this keyword to an existing IDL Graphic reference to make that window be the current window and direct the new graphic to that window.
DEPTH_CUE
Set this keyword to a two-element vector [bright, dim] specifying the near and far planes for depth cueing, in normalized units. Depth cueing causes graphics objects that are further away to fade into the background. The first element is where the fade starts to take effect, while the second element is where the objects are completely transparent. Negative values are closer to the eye, while positive values are farther from the eye. The default value is [0, 0] which disables depth cueing. A typical value would be [0, 1], which would cause objects to start to fade at the mid-plane of the window, and completely fade out at a normalized eye distance of 1.
DEVICE
Set this keyword if values are specified in device coordinates (pixels) for the MARGIN and POSITION keywords. (Normalized coordinates are the default for these keywords.)
DIMENSIONS
Set this keyword to a two-element vector of the form [width, height] to specify the window dimensions in pixels. If you do not specify a value for DIMENSIONS, IDL by default uses the values of the IDL_GR_WIN_HEIGHT and IDL_GR_WIN_WIDTH preferences for Windows platforms or the IDL_GR_X_HEIGHT and IDL_GR_X_WIDTH preferences for X Windows systems on UNIX.
DRAG_QUALITY
Set this keyword to 0, 1, or 2 to control the rendering quality and performance during moves, transformations, and rotations initiated with the mouse. The default value is 2, which maintains full rendering quality during mouse interactions. Set to 1 to reduce the drawing quality, or to 0 to further reduce or in some cases disable drawing during dragging or resizing.
LAYOUT
Set this keyword to a three-element vector [ncol, nrow, index] that arranges graphics in a grid. The first dimension ncol is the number of columns in the grid, nrow is the number of rows, and index is the grid position at which to place the graphic (starting at element 1). This keyword is ignored if either OVERPLOT or POSITION is specified.
LOCATION
Set this keyword to a two-element vector [X offset, Y offset] giving the window's screen offset in pixels.
MARGIN
Set this keyword to the current graphic’s margin values in the layout specified by the LAYOUT property. Use a scalar value to set the same margin on all sides, or use a four-element vector [left, bottom, right, top] to specify different margins on each side.
By default, margin values are expressed in normalized units ranging from 0.0 to 0.5. If the DEVICE keyword is set, the values are given in device units (pixels).
This keyword is ignored if either OVERPLOT or POSITION is specified.
NODATA
Set this keyword to 1 to create the graphic, but without any data attached to it. The axes and title (if present) are also created and displayed. If the OVERPLOT keyword is specified, axis ranges will not change.
Note: You must still provide valid input arguments. The data range of the input arguments are used to automatically set the range of the axes. The [XYZ]RANGE properties may be used to override these default ranges.
OVERPLOT
Set this keyword to 1 (one) to place the graphic on top of the existing graphic in the current window. If no current window exists, a new window is created.
Set this keyword to an existing IDL Graphic reference to direct the new graphic to the window specified by the provided IDL Graphic reference.
Properties
ANTIALIAS
By default anti-aliasing is used when drawing symbols. Set this property to 0 to disable anti-aliasing.
ASPECT_RATIO
A floating point value indicating the ratio of the Y dimension to the X dimension in data units. If this property is set to a nonzero value, the aspect ratio will be preserved as the graphic is stretched or shrunk. The default value is 0 for all graphics except images, meaning that the aspect ratio is not fixed, but is allowed to change as the graphic is stretched or shrunk.
AXES (Get Only)
This property retrieves an array that contains all of the AXIS objects within the visualization. For example, for a plot visualization:
p = PLOT(/TEST)
ax = p.AXES
ax[0].TITLE = 'X axis'
ax[1].TITLE = 'Y axis'
ax[2].HIDE = 1
ax[3].HIDE = 1
See AXIS for a list of the available properties.
BACKGROUND_COLOR
Set this property to a string or RGB vector indicating the graphic's background color. The default value is [255, 255, 255] (white). Set this property to a scalar value to remove the background color.
Tip: To set the background color of the entire window, retrieve the window object using the WINDOW property, and set the BACKGROUND_COLOR on the window object.
BACKGROUND_TRANSPARENCY
Set this property to an integer between 0 and 100 giving the percent transparency of the background color. The default is 100 (completely transparent).
Note: If the BACKGROUND_COLOR property is changed and the current background transparency is 100, then the BACKGROUND_TRANSPARENCY will be automatically set to 0 (opaque) so that you can see the new color.
CLIP
Set this property to 1 to clip portions of the graphic that lie outside of the dataspace range, or to 0 to disable clipping. The default is 1.
CROSSHAIR (Get Only)
Use this property to retrieve a reference to the Crosshair graphic. All graphics objects within the same set of axes share a single Crosshair graphic. For Plot graphics the default behavior is to display the crosshair when a Mouse_Down event is received. For other graphics the crosshair is disabled. The STYLE property may be used to automatically draw the crosshair, while the LOCATION property may be used to manually draw the crosshair.
You can get and set the following properties on the retrieved crosshair:
|
Property |
Description |
|
ANTIALIAS |
Set to 1 to enable anti-aliasing for the lines.
|
|
COLOR |
A string or RGB vector containing the color.
|
|
HIDE |
Set to 1 to hide the crosshair, 0 to show.
|
|
INTERPOLATE |
Set to 1 to force interpolation between Plot data points when SNAP is active. For other graphics this property is ignored. The default is 0.
|
|
LINESTYLE |
An integer or string giving the line style. The default is 'dot'. See Linestyle Values for additional options.
|
|
LOCATION |
The location at which to draw the crosshair. For Plot graphics, if SNAP is enabled, then only the X coordinate needs to be supplied. Otherwise, LOCATION should be set to a two-element vector [X, Y] for two-dimensional graphics or [X, Y, Z] for three-dimensional graphics. If STYLE is currently "None", then setting the LOCATION will automatically set the STYLE to "Manual".
|
|
NAME |
The name of the graphic.
|
|
SNAP |
Set to 1 to snap the crosshair to the nearest Plot data point. For other graphics this property is ignored. The default is 1.
|
|
STYLE |
An integer or string giving the crosshair style. Possible values are:
0 - "None" - never draw the crosshair. This is the default for all graphics except 2D plots.
1 - "Manual" - draw the crosshair using the LOCATION property.
2 - "Auto" - automatically draw the crosshair. This is the default for 2D plots.
|
|
THICK |
The thickness of the lines. The default is 1.
|
|
TRANSPARENCY |
The percent transparency of the lines. The default is 50.
|
|
UVALUE |
An IDL variable of any data type.
|
For example, use the CROSSHAIR property to draw a crosshair on an image:
im = IMAGE(/TEST, TRANSPARENCY=50, AXIS_STYLE=2)
c = im.CROSSHAIR
c.COLOR = 'red'
c.THICK = 2
c.LOCATION = [300, 200]
See Creating Functions to Control Mouse Events for a more detailed crosshair example.
EYE
A floating-point value that specifies the distance from the eyepoint to the viewplane (Z=0). The default is 4.0. The eyepoint is always centered within the viewplane rectangle. IDL converts, maintains, and returns this data as double-precision floating-point.
FONT_COLOR
Set this property to a string or RGB vector that specifies the text color of the title and axes (if present). The default value is "black".
FONT_NAME
Set this property equal to a string specifying the IDL or system font for the title and axes (if present). The default value is “Helvetica”.
FONT_SIZE
Set this property equal to an integer specifying the font size for the title and axes (if present). The default value is 12 points.
FONT_STYLE
Set this property equal to an integer or a string specifying the font style for the title and axes (if present). Allowed values are:
|
Integer |
String |
Resulting Style |
|
0 |
"Normal" or "rm"
|
Default (roman) |
|
1 |
"Bold" or "bf" |
Bold |
|
2 |
"Italic" or "it"
|
Italic |
|
3 |
"Bold italic" or "bi"
|
Bold italic |
HIDE
Set this property to 1 to hide the graphic. Set HIDE to 0 to show the graphic.
MAGNITUDE
An M-element vector of indices into the color table for the color of each data point. If the values supplied are not of type byte, they are scaled to the byte range using BYTSCL and the current number of colors in the RGB_TABLE property. If indices are supplied but no colors are provided with RGB_TABLE, a default grayscale ramp is used. If the number of indices specified is less than the number of vertices, the colors are repeated cyclically. If the number of indices specified is greater than the number of vertices, only the first M indices will be used.
MAX_VALUE
The maximum value to be plotted. If this property is set, data values greater than the value of MAX_VALUE are treated as missing data and are not plotted.
Note: The IEEE floating point value NaN is also treated as missing data.
MIN_VALUE
The minimum value to be plotted. If this property is set, data values less than the value of MIN_VALUE are treated as missing data and are not plotted.
Note: The IEEE floating point value NaN is also treated as missing data.
NAME
A string that specifies the name of the graphic. The name can be used to retrieve the graphic using the brackets array notation. If NAME is not set then a default name is chosen based on the graphic type.
POSITION
Set this property to a four-element vector that determines the position of the graphic within the window on the XY plane. The coordinates [X1, Y1, X2, Y2] define the lower left and upper right corners of the graphic. Coordinates are expressed in normalized units ranging from 0.0 to 1.0. On creation, if the DEVICE keyword is set, the units are given in device units (pixels).
Note: After creation, you can set the POSITION to either a two or four-element vector. If you provide two elements, IDL translates the center of the graphic to that position. If you provide four elements, IDL translates and scales the graphic to fit the position.
RGB_TABLE
The number of the predefined IDL color table, or a 3 x 256 or 256 x 3 byte array containing color values to use for vertex colors. If the values supplied are not of type byte, they are scaled to the byte range using BYTSCL. Use the MAGNITUDE property to specify indices that select colors from the values specified with RGB_TABLE.
SYM_COLOR
Set this property to a string or RGB vector that specifies the color of the plot symbol. If the MAGNITUDE property is set it will override SYM_COLOR.
SYM_FILLED
Set this property to 1 to fill the symbols.
SYM_FILL_COLOR
Set this property to a string or RGB vector that specifies the color of the filled portion of the symbol. If this property is not set then the symbol fill color will match the SYM_COLOR.
SYM_OBJECT
Set this property equal to an object reference to be used for the plotting symbol. The SYM_OBJECT may be either an IDLgrModel object or an atomic graphics object.
SYM_SIZE
A floating point value specifying the size of the plot symbol. A value of 1.0 produces a symbol that is 10% of the width/height of the plot.
SYM_THICK
A floating point value from 1.0 to 10.0 that specifies the thickness (in points) of the plot symbol.
SYM_TRANSPARENCY
An integer between 0 and 100 that specifies the percent transparency of the symbols. The default value is 0.
SYMBOL
A string giving the symbol name. "Diamond" is the default. Allowed values are:
|
"None"
"Plus" or "+"
"Asterisk" or "*"
"Period" or "dot"
"Diamond" or "D"
"Triangle" or "tu"
"Square" or "s"
"X"
"Greater_than" or ">"
|
"Less_than" or "<"
"Triangle_down" or "td"
"Triangle_left" or "tl"
"Triangle_right" or "tr"
"Tri_up" or "Tu"
"Tri_down" or "Td"
"Tri_left" or "Tl"
"Tri_right" or "Tr"
|
"Thin_diamond" or "d"
"Pentagon" or "p"
"Hexagon_1" or "h"
"Hexagon_2" or "H"
"Vline" or "|"
"Hline" or "_"
"Star" or "S"
"Circle" or "o"
|
Note that all plot symbol names are case sensitive.
TITLE
Set this property to a string specifying a title. The title properties may be modified using FONT_COLOR, FONT_NAME, FONT_SIZE, and FONT_STYLE. After creation the TITLE property may be used to retrieve a reference to the title text object, and the TEXT properties may be used to modify the title object.
You can also add Greek letters and mathematical symbols using a TeX-like syntax. These symbols need to be enclosed within a pair of "$" characters. See Adding Mathematical Symbols and Greek Letters to the Text String for details on the available symbols.
UVALUE
Set this property to an IDL variable of any data type.
WINDOW (Get Only)
This property retrieves a reference to the WINDOW object which contains the graphic.
WINDOW_TITLE
Set this property to the title of the IDL Graphic window. The title is displayed in the window's title bar.
XRANGE
A two-element vector giving the X data range to plot. The default behavior is to plot the entire data range.
YRANGE
A two-element vector giving the Y data range to plot. The default behavior is to plot the entire data range.
ZCLIP
A two element floating-point vector representing the near and far clipping planes to be applied to the objects in this view. The vector should take the form [near, far]. By default, these values are [1, -1]. IDL converts, maintains, and returns this data as double-precision floating-point.
ZRANGE
A two-element vector giving the Z data range to plot. The default behavior is to plot the entire data range.
Version History
Resources and References
Data used in the SCATTERPLOT3D example is simulated but based on concepts in:
Brown, C.S., M.F. Meier, and A. Post. Calving Speed of Alaska Tidewater Glaciers, with Application to Columbia Glacier: USGS Professional Paper 1258-C. United States Government Printing Office, 1982.
See Also
!COLOR, BARPLOT,
ERRORPLOT, Formatting IDL Graphics Symbols and Lines, Graphics Window Interface,
LEGEND,
PLOT3D, PLOT,
POLARPLOT, SCATTERPLOT,
Using IDL graphics