This function constructs an ENVIRaster from an array of source rasters that overlap or contain gaps in coverage. ENVIIrregularGridMetaspatialRaster crops or pads the source rasters to a standard tile size if needed, then it tiles them into one raster.
The most common use for this function is with QuickBird images in DigitalGlobe tiled format (*.til) that overlap in coverage. When you use File > Open to select a .til file in the user interface, ENVI automatically assembles the tiles to construct a virtual raster. However, the ENVIIrregularGridMetaspatialRaster function was designed to give ENVI programmers control over the offsets and tile sizes needed to construct a new raster from individual source rasters.
The result is a virtual raster, which has some additional considerations with regard to methods and properties. See Virtual Rasters for more information, including how they differ from ENVITasks.
The equivalent task is BuildIrregularGridMetaspatialRaster.
Example
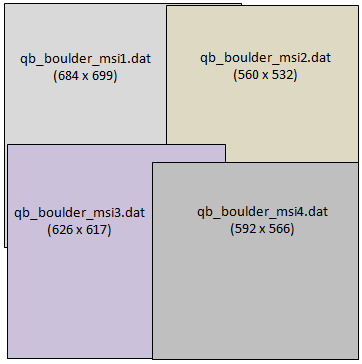
This example creates a metaspatial raster from four source rasters. The source files are available from our ENVI Tutorials web page. Click the API Gridding Examples link to download the .zip file to your machine, then unzip the files. Update the file references in the example with the correct locations.
Each source raster overlaps the others. The metaspatial raster created in this example will have a fixed tile size of 512 x 512 pixels:
e = ENVI()
offsets = LonArr(2,2,2)
file1 = 'qb_boulder_msi1.dat'
raster1 = e.OpenRaster(file1)
offsets[0,0,0] = 0
offsets[0,0,1] = 0
file2 = 'qb_boulder_msi2.dat'
raster2 = e.OpenRaster(file2)
offsets[1,0,0] = 464
offsets[1,0,1] = 0
file3 = 'qb_boulder_msi3.dat'
raster3 = e.OpenRaster(file3)
offsets[0,1,0] = 10
offsets[0,1,1] = 399
file4 = 'qb_boulder_msi4.dat'
raster4 = e.OpenRaster(file4)
offsets[1,1,0] = 425
offsets[1,1,1] = 453
inputRasters = [[raster1, raster2], [raster3, raster4]]
tileSize = [512,512]
msRaster = ENVIIrregularGridMetaspatialRaster(inputRasters, $
tileSize, offsets)
view = e.GetView()
layer = view.CreateLayer(msRaster)
view.Zoom, /FULL_EXTENT
Syntax
Result = ENVIIrregularGridMetaspatialRaster(Input_Rasters, Tile_Size, Offsets [, Keywords=value])
Return Value
This routine returns a reference to an ENVIRaster. The returned raster will be cast to the highest data type among all the source rasters.
Arguments
Input_Rasters
Specify a 2D array of input ENVIRasters. The following rules apply:
- Specify empty tiles with null objects by calling the IDL Obj_New routine instead of using ENVIRasters.
- Metadata values are passed from the source rasters to the virtual raster only if the values are the same in all source rasters.
- Source rasters do not need to be georeferenced. If the top-left tile contains a spatial reference, that reference will be used for the virtual raster. You can override the spatial reference by using the SPATIALREF keyword.
-
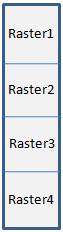
The order of the array elements determines the layout of the tiles in the metaspatial raster. Here are some examples:
SourceRasters = [raster1, raster2, raster3, raster4]
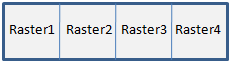
SourceRasters = [[raster1, raster2], [raster3, raster4]]

[[raster1], [raster2], [raster3], [raster4]]
Tile_Size
Specify a 2D array indicating the desired size of each tile, in number of pixels. Use this convention: [xSize, ySize]. Each source raster will be cropped or padded with "no data" values to fit the tile size.
Offsets
Offsets are zero-based pixel coordinates that represent the top-left corner of each raster with respect to the top-left corner of the metaspatial raster. Specify an m x n x 2 array of offsets corresponding to the m x n array of source rasters, along with a column and row offset for each array.
For example, the layout of source rasters in the code example above is specified with a 2 x 2 array:
sourceRasters = [[raster1, raster2], [raster3, raster4]]
Offsets is a 2 x 2 x 2 array in this case. To further illustrate this example, the offsets for the upper-right image (raster2) are as follows:
offsets[1,0,0] = 464
offsets[1,0,1] = 0
Where:
- [1,0,0] is the array index for the column, and 464 is its offset value
- [1,0,1] is the array index for the row, and 0 is its offset value.
This means that pixel location (464,0) in raster2 will be the upper-right corner of the associated tile in the virtual raster.
Methods
This virtual raster inherits methods and properties from ENVIRaster; however the following methods will override the ENVIRaster methods:
Dehydrate
Hydrate
Keywords
ERROR (optional)
Set this keyword to a named variable that will contain any error message issued during execution of this routine. If no error occurs, the ERROR variable will be set to a null string (''). If an error occurs and the routine is a function, then the function result will be undefined.
When this keyword is not set and an error occurs, ENVI returns to the caller and execution halts. In this case, the error message is contained within !ERROR_STATE and can be caught using IDL's CATCH routine. See IDL Help for more information on !ERROR_STATE and CATCH.
See Manage Errors for more information on error handling in ENVI programming.
NAME
Specify a string that identifies the raster.
SPATIALREF (optional)
Set this keyword to an ENVIStandardRasterSpatialRef, ENVIPseudoRasterSpatialRef, or ENVIRPCRasterSpatialRef object to be used by the output raster mosaic. If this keyword is not specified, then the SPATIALREF property of the upper left corner raster will be used, if possible. If the upper left corner raster is a NullObject, or if it does not have a SPATIALREF value, then the output raster will not have any spatial reference associated with it.
Version History
|
ENVI 5.2.1 |
Introduced |
|
ENVI 5.3.1 |
Documented the dehydrated form of this virtual raster
|
|
ENVI 5.4 |
Added Dehydrate and Hydrate methods; added NAME keyword
|
See Also
ENVIRaster, ENVIMetaspatialRaster, BuildMetaspatialRaster Task, BuildIrregularGridMetaspatialRaster Task