An activation function is a mathematical tool used in machine learning to impart non-linearities into linear systems. Choosing the proper activation function(s) is an important step in designing your neural network. The IDLmlafSoftExponential activation function is implemented with the following formula:
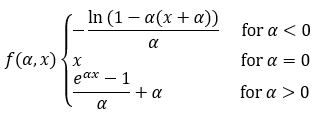
Example
Compile_opt idl2
Data = findgen(10)
actFunc = IDLmlafSoftExponential(1.0)
Print, actFunc(data)
Syntax
actFunc = IDLmlafSoftExponential(Alpha)
Result = actFunc(X [, GRADIENT=value])
Note: IDL activation functions work by overloading the function operator. To avoid compilation problems, make sure that every routine that uses an activation function contains the statement:
Compile_opt idl2
Arguments
Alpha
Specify a number that will serve as alpha coefficient for the activation function (see the formula).
Keywords
GRADIENT (optional)
Set this keyword to a named variable to receive the gradient of the activation function at each point in the input X array. The output gradient will have the same dimensions as the input X array.
Version History
See Also
IDLmlafArcTan, IDLmlafBentIdentity, IDLmlafBinaryStep, IDLmlafELU, IDLmlafGaussian, IDLmlafIdentity, IDLmlafISRLU, IDLmlafISRU, IDLmlafLogistic, IDLmlafPReLU, IDLmlafReLU, IDLmlafSinc, IDLmlafSinusoid, IDLmlafSoftmax, IDLmlafSoftPlus, IDLmlafSoftSign, IDLmlafTanH