Highlights in this release include the following:
ONNX for Classification Workflows
This release of ENVI Deep Learning introduces ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange), which is now used for all classification workflows. ONNX is a standard AI model format that many AI frameworks support, and it enables models that were trained in different frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch, etc.) to run in ENVI Deep Learning.
The benefits of using ONNX include:
- Models can be trained in the framework of choice, then configured to run in ENVI Deep Learning object detection and pixel segmentation workflows.
- Models that are trained in ENVI Deep Learning 4.0 will be created as ONNX models.
- Classification workflows using ONNX run 2-4 times faster overall as compared to ENVI Deep Learning 3.0.
- GPU or CPU processing is available (GPU processing is still recommended in most cases, for a better user experience).
For more information on ONNX, see ONNX Overview.
For information on the compatibility of ENVI Deep Learning 3.0 models in version 4.0, see the Compatibility section of this topic.
Integration With the Analytics Repository
This release of ENVI Deep Learning is integrated with the Analytics Repository, which is a cross-platform server that automates managing file dependencies across multiple machines. Models and other files can be published to the repository and downloaded to other machines, enabling you to create and share analytic-based content across your organizations.
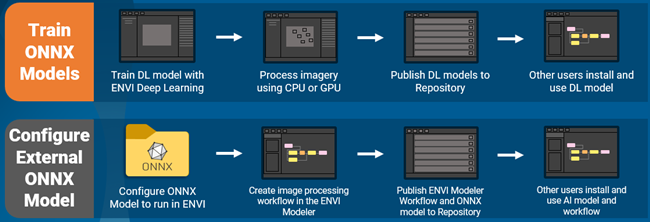
See the following for additional information:
RT-DETR V2 Used for Object Detection
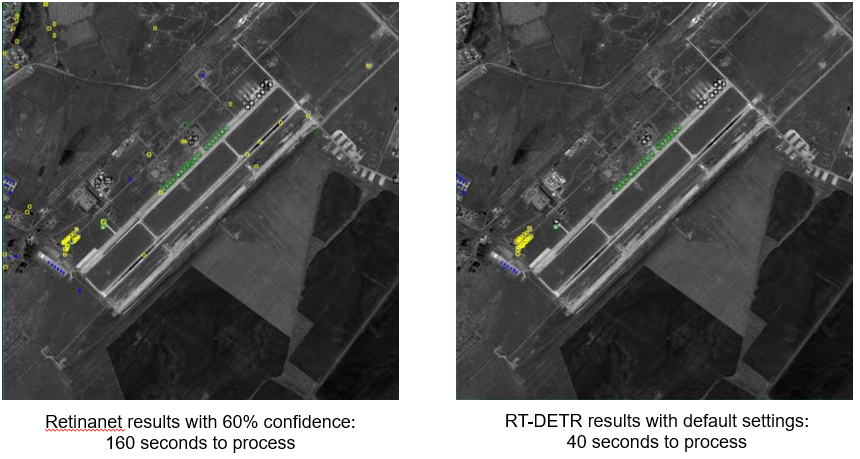
For object detection classification, this release replaces Retinanet with RT-DETR V2. RT-DETR V2 is superior to Retinanet at detecting targets, with processing speeds 3-4 times faster with the same amount of training.
This, along with other changes, impacts all object detection models created in ENVI Deep Learing 3.0. For information on compatibility see the Compatibility section in this topic.
Build Object Detection Rasters from COCO
ENVI Deep Learning now supports building object detection rasters from COCO (Common Objects in Context) files. This tool takes a JSON dataset that contains COCO formatted annotations and generates object detection rasters. Each raster will correspond to labeled regions of interest defined in the COCO input annotations.
See Build Object Detection Rasters From COCO for details.
Optimized Data Preparation
A new data preparation workflow supports standard practices for creating raster data for use in deep learning, including the use of stretch and RGB images.
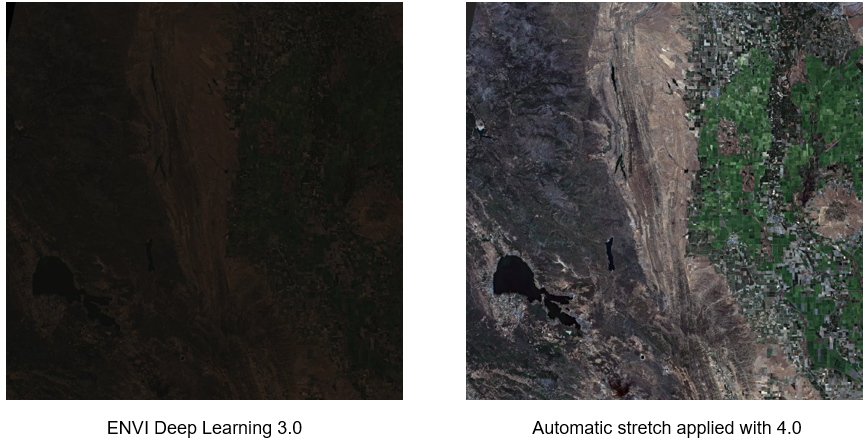
Data Stretch
ENVI Deep Learning will apply an automatic visual stretch to data, just as ENVI does when you open imagery. For non-byte data, automatically applying the stretch will significantly improve the visual contrast for images and the ability of deep learning models to detect features.
You can apply an additional stretch to images to further enhance the display and reduce noise.

Visual RGB Raster
You can optionally create a 3-band output raster with the Visual RGB option that has been added to the classification parameter settings. It will create an RGB from SAR, panchromatic, MSI, CIR, and model datasets, allowing you to mix and match sensor types for more widely usable models.
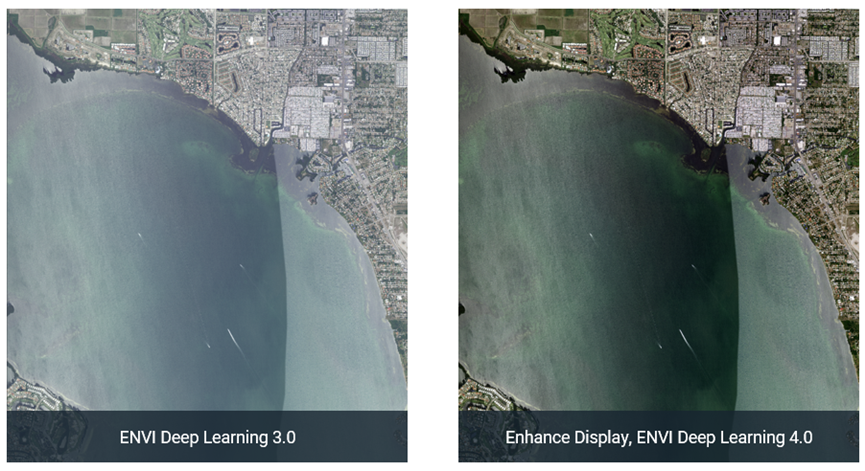
Enhance Visual Display
With the Enhance Display option that has been added to the classification parameter settings, you can enhance the visual display of datasets when you create a new deep learning raster or process imagery. This option removes visual noise, providing sharper, more vivid imagery that makes it easier to see features. It is useful for aerial sensors that have background noise.

See the following for more information the new parameters:
Compatibility
Because of the significant changes made in this release, models created in ENVI Deep Learning 3.0 will not be compatible in ENVI Deep Learning 4.0. To make the 3.0 models compatible, you need to do the following:
- All pixel segmentation and grid models trained in version 3.0 will need to be re-trained.
- All object detection models will need to be re-written to work with the addition of RT-DETR V2.
All ENVI Deep Learning 3.0 tasks and tools containing "TensorFlow" in their names have been renamed and updated with new parameters. See Renamed Tools and Renamed Tasks and Objects in this topic for details.
To help migrate models, ENVI 6.1 and ENVI Deep Learning 3.0 can be installed side-by-side with ENVI 6.2 and ENVI Deep Learning 4.0.
The ENVITensorBoard procedure allows you change the location of TensorBoard so you can organize your training.
Performance Improvements
-
Initialization in ENVI Deep Learning 3.0 took 30-45 seconds (depending on your hardware). In ENVI Deep Learning 4.0, start-up time has dramatically improved and now takes just a few seconds to initialize. Speed has also improved for every process, as follows:
- Object Detection: RT-DETR processing time is 3-4x faster than Retinanet (this depends on your architecture, but it is overall much faster).
- Pixel Segmentation: Processing time is approximately 2 times faster.
- Grid: Processing time is approximately 2 times faster.
-
ResNet50v2 and ResNet101v2 support has been added, enhancing the core neural network architecture used for pixel segmentation and grid-based analysis.
Installer Updates
ENVI Machine Learning is no longer bundled with the ENVI Deep Learning installer. Now it is a separate installer that is included with the ENVI download.
New and Renamed Tools
New Tools
Renamed Tools
The following tools were renamed and updated with new parameters in this release:
The following tools replace Edit TensorFlow Model Metadata from ENVI Deep Learning 3.0:
New and Renamed Tasks and Objects
New Tasks
Renamed Tasks and Objects
The following tasks were renamed in this release. Refer to the Version History section of each topic for details on new and updated parameters.
The following objects replace ENVITensorFlowGridModel, ENVITensorFlowModel, and ENVITensorFlowObjectModel from ENVI Deep Learning 3.0:
See Also
See What's New (Previous ENVI Deep Learning Releases) for an archive of What's New information.