Deep Learning Grid Classification
Tutorial: Optimized Pixel Classification Using a Grid Model Tutorial
Use the Deep Learning Grid Classification tool to classify a raster using a trained ENVI Deep Learning ONNX grid model. The output is a classification vector.
You can also write a script to classify a raster using the DeepLearningGridClassification task.
Follow these steps:
-
In the ENVI Toolbox, select Deep Learning > Grid > Deep Learning Grid Classification. The Deep Learning Grid Classification dialog appears with the Main tab selected.
You can also access the Deep Learning Grid Classification dialog through the Deep Learning Guide Map with the following button sequence: Grid > Grid Classification. An advantage of this option is that if you access the Deep Learning Labeling Tool through the Guide Map and use it to create label rasters and train a model, the Guide Map knows about the trained model and automatically populates the Input Model field in the dialog.
- In the Input Raster field, select a raster to classify. It must contain at least as many bands as the raster that was used to train the model.
- In the Input Model field, select an ONNX file (.envi.onnx) that was designed for grid-based analysis to classify the input raster.
- In the Confidence Threshold field, enter a confidence score of 0.0 to 1.0. Grid cells with a score less than this value will be discarded. The default is 0.2.
-
For Enhance Display, select Yes if you want to apply an additional small stretch to the processed data to suppress noise and enhance feature visibility. The optional stretch is effective for improving visual clarity in imagery acquired from aerial platforms or sensors with higher noise profiles.
-
For Visual RGB, select Yes if you want to encode the output raster as a three-band RGB composite (red, green, blue) for color image processing. This ensures consistent band selection from ENVI display types (such as RGB, CIR, and pan) and supports integration of diverse data sources (such as MSI, panchromatic, and VNIR) without band mismatch.
- To set advanced parameters for processing, select the Advanced tab.
-
Use the CUDA Device ID parameter to explicitly control GPU selection in multi-GPU environments when you choose CUDA as the Processing Runtime. Optionally enter a target GPU device ID. If you provide a valid ID, the classification task will execute on the specified CUDA-enabled GPU. If the ID is omitted or invalid, the system defaults to GPU device 0.
-
From the Processing Runtime field, select one of the following execution environments for the classification task:
- CUDA: (Default) Uses NVIDIA GPU acceleration for optimal performance and faster processing
- CPU: Ensures compatibility on systems without GPU support, but with reduced processing speeds.
- In the Output Classification Vector field, select a path and filename for the output classification vector (.shp).
-
Enable the Display result check box to display the output in the view when processing is complete.
-
To reuse these task settings in future ENVI sessions, save them to a file. Click the down arrow 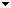 next to the OK button and select Save Parameter Values, then specify the location and filename to save to. Note that some parameter types, such as rasters, vectors, and ROIs, will not be saved with the file. To apply the saved task settings, click the down arrow
next to the OK button and select Save Parameter Values, then specify the location and filename to save to. Note that some parameter types, such as rasters, vectors, and ROIs, will not be saved with the file. To apply the saved task settings, click the down arrow  and select Restore Parameter Values, then select the file where you previously stored your settings.
and select Restore Parameter Values, then select the file where you previously stored your settings.
-
To run the process in the background, click the down arrow  and select Run Task in the Background. If an ENVI Server has been set up on the network, the Run Task on remote ENVI Server name is also available. The ENVI Server Job Console will show the progress of the job and will provide a link to display the result when processing is complete. See the ENVI Servers topic in ENVI Help for more information.
and select Run Task in the Background. If an ENVI Server has been set up on the network, the Run Task on remote ENVI Server name is also available. The ENVI Server Job Console will show the progress of the job and will provide a link to display the result when processing is complete. See the ENVI Servers topic in ENVI Help for more information.
- Click OK.
Evaluate the Results
The output classification vector displays on top of the raster used for classification. Green boxes appear around areas containing features of interest. The following image shows an example of a grid vector overlaid on the raster used during classification. Areas that do not contain a grid cell (the green boxes) represent areas where no features were detected for the specified confidence threshold. This example uses the ENVI Deep Learning Grid Tutorial data with a confidence threshold of 0.90, searching for small boats.
Follow these steps to overlay the output classification vector on the Input Raster:
-
Display the Input Raster in the current view.
-
In the Layer Manager, click and drag the Input Raster below the vector classification output.
You can also view confidence values for each area of interest identified by the green boxes. This may help in determining whether your confidence threshold was set too high or too low, and help assess the accuracy of your model.
- In the Layer Manager right click the classification vector layer and select Filter Records by Attribute.
-
In the Filter by Attributes dialog, select the Class_ID drop-down list, then select Confidence.
-
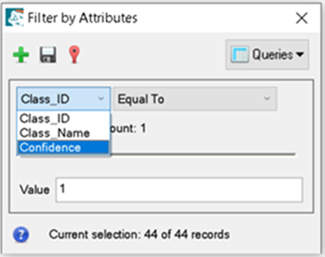
Move the slider bar to the far right to set the confidence search Value to 0.999. You can move the slider back and forth to see what a target area's confidence values are. Green squares will turn black to show the areas with the selected confidence value.
Below is an example of areas identified with a 0.999% confidence that they contain a boat feature.
See Also
Train Deep Learning Grid Models, Deep Learning Optimized Object Classification, Deep Learning Optimized Pixel Classification