You can create custom functions to handle keyboard events in a graphics WINDOW or in a WIDGET_WINDOW. These functions must use the syntax described below.
Each function must return a value of 0 to turn off default event handling or 1 to perform default event handling.
Tip: Instead of creating a separate function for each event handler, you may find it convenient to use a custom event handling class along with the EVENT_HANDLER property. See Creating an Event Handler Class to Control Events for details on how to write this object class.
Syntax
Result = FUNCTION_NAME(Window, IsASCII, Character, KeyValue, X, Y, Press, Release, KeyMods)
Where FUNCTION_NAME is a unique name for the function, which will be called from one of the keyboard event handling keywords of WINDOW or WIDGET_WINDOW. Avoid using generic names such as "KeyboardHandler" to prevent name collisions with other applications using event handlers.
Arguments
Window
The object reference of the window in which a keyboard event happened.
IsASCII
A scalar byte value that indicates whether the keyboard event corresponds to an ASCII character. If IsASCII is non-zero, the Character argument will be set to a byte value corresponding to the character of the pressed key. If IsASCII is zero, the KeySymbol argument will be set to a numeric value indicating the key that was pressed.
Character
If IsASCII is non-zero, this argument is set to a byte value corresponding to the ASCII character of the key that was pressed. Otherwise, this argument is set to zero.
KeyValue
If IsASCII is zero, this argument is set to a value that indicates the key that was pressed. Otherwise, this argument is set to zero. Possible values are:
|
Value |
Key |
|
1 |
Shift |
|
2 |
Control |
|
3 |
Caps lock |
|
4 |
Alt |
|
5 |
Left |
|
6 |
Right |
|
7 |
Up |
|
8 |
Down |
|
9 |
Page up |
|
10 |
Page down |
|
11 |
Home |
|
12 |
End |
Note: On East Asian (Chinese, Japanese, Korean) localized Windows operating systems with an Asian language pack installed, characters entered in the Windows Input Method Manager (IMM)composition window are returned in the the KeyValue argument as unsigned integers representing a Wide character (Unicode value). The I18N_WIDECHARTOMULTIBYTE routine can convert these characters to multibyte strings. For more information, see Internationalizing Code.
X
The position to the right of the lower left corner of the drawable area, in device coordinates (pixels).
Y
The position above the lower left corner of the drawable area, in device coordinates (pixels).
Press
The value indicating that this event represents a key press. This argument is non-zero if the event is the result of pressing the key.
Release
The value indicating that this event represents a key release. This argument is non-zero if the event is the result of releasing the key.
KeyMods
The value containing a bitwise mask indicating which modifier keys are active at the time of the keyboard event. If a bit is zero, the key is up; if the bit is set, the key is pressed. The following table describes the bits in this bit mask. Possible values are:
|
Value |
Modifier Key |
|
1 |
Shift |
|
2 |
Control |
|
4 |
Caps lock |
|
8 |
Alt |
Example
In the following example code, the KeyboardEventsTestHandler function creates graphic element selections based on the keyboard character that is typed. Copy this code into a new IDL file and compile it. The example below this one is a test that you can run to see these selections work.
FUNCTION KeyboardEventsTestHandler, Window, $
IsASCII, Character, KeyValue, X, Y, Press, Release, KeyMods
print, 'KeyboardHandler'
help, Window, $
IsASCII, Character, KeyValue, X, Y, Press, Release, KeyMods
IF Release then return, 1
graphics = Window.uValue
graphics[0].select, /clear
FOREACH graphic, graphics do begin
CASE string(character) OF
't': if ISA(graphic, 'TEXT') then graphic.select, /ADD
'c': if ISA(graphic, 'ELLIPSE') then graphic.select, /ADD
'l': if ISA(graphic, 'POLYLINE') then graphic.select, /ADD
'p': if ISA(graphic, 'POLYGON') then graphic.select, /ADD
ELSE:
ENDCASE
ENDFOREACH
Window.refresh
RETURN, 0
END
Keyboard Character Selection Example
Run the following code example to test the event handling functions defined in the previous code example.
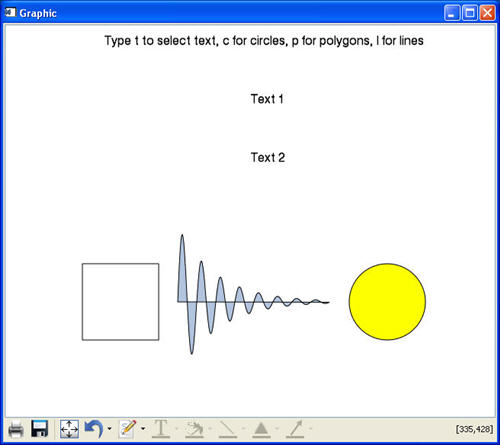
PRO KeyboardEventsTest
window = window()
text1=text(.2, .95, 'Type t to select text, c for circles, p for polygons, l for lines')
text2=text(.5, .8, 'Text 1')
text3=text(.5, .65, 'Text 2')
circle = ELLIPSE(500, 150, MAJOR=50, /device, $
FILL_COLOR="yellow")
x = indgen(200)+225
y = SIN(2.0*FINDGEN(200)*!PI/25.0)*EXP(-0.02*FINDGEN(200))*100 + 150
polygon = POLYGON(x, y, /device, $
/FILL_BACKGROUND, FILL_COLOR=!COLOR.LIGHT_STEEL_BLUE)
x = [100, 200, 200, 100, 100]
y = [100, 100, 200, 200, 100]
line = POLYLINE(x, y, /DEVICE)
window.uValue = [text1, text2, text3, circle, polygon, line]
window.KEYBOARD_HANDLER='KeyboardEventsTestHandler'
END