The IMSL_SP_MVMUL function computes a matrix-vector product involving sparse matrix and a dense vector.
This routine requires an IDL Advanced Math and Stats license. For more information, contact your sales or technical support representative.
The IMSL_SP_MVMUL function computes a matrix-vector product involving a sparse matrix and a dense vector.
If A is stored in coordinate format, then the arguments N_Rows, N_Cols, A, and x should be used. If the keyword SYMMETRIC is set, then Ax + ATx – diag(A) is returned.
If A is a banded, then the arguments N_Rows, N_Cols, N_Lca, N_Uca, A, and X should be used. If the keyword SYMMETRIC is set, then A must be in band symmetric storage mode, and the number of codiagonals should be used for both N_Lca and N_Uca.
Examples
Example 1
This example computes Ax, where A is stored in coordinate format.
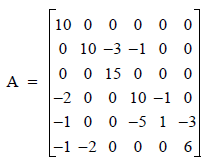
Let xT = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
A = replicate(imsl_f_sp_elem, 15)
a(*).row = [0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5]
a(*).col = [0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 0, 3, 4, 0, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 5]
a(*).val = [10, 10, -3, -1, 15, -2, 10, -1, -1, -5, $
1, -3, -1, -2, 6]
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
ax = IMSL_SP_MVMUL(6, 6, a, x)
PM, ax
10.000000
7.0000000
45.000000
33.000000
-34.000000
31.000000
Example 2
This example computes Ax, where A is stored in band mode. Consider the 1000 x 1000 banded matrix below:
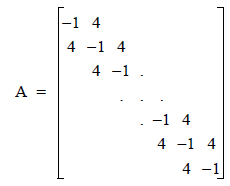
Let x(*) = 2.
n_rows = 1000L
nlca = 1L
nuca = 1L
a = DBLARR(n_rows*(nlca+nuca+1))
a(1:n_rows-1) = 4
a(n_rows:2*n_rows-1) = -1
a(2*n_rows:*) = 4
x = DBLARR(n_rows)
x(*) = 2
expected = DBLARR(n_rows)
expected(*) = 14
expected(0) = 6
expected(n_rows-1) = 6
ax = IMSL_SP_MVMUL(n_rows, n_rows, nlca, nuca, a, x)
PRINT, TOTAL(ABS(ax-expected))
0.0000000
Example 3
This example computes Ax, where A is stored in band symmetric mode. Let
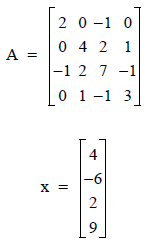
n = 4L
ncoda = 2L
a = DBLARR((ncoda+1)*n)
a(0:n-1) = [0, 0, -1, 1]
a(n:2L*n-1) = [0, 0, 2, -1]
a(2L*n:*) = [2, 4, 7, 3]
x = [4, -6, 2, 9]
ax = IMSL_SP_MVMUL(n, n, ncoda, ncoda, a, x, /Symmetric)
PM, ax
6.0000000
-11.000000
-11.000000
19.000000
Syntax
Matrix stored in coordinate format:
Result = IMSL_SP_MVMUL(N_Rows, N_Cols, A, X [, SYMMETRIC=value])
Matrix stored in band format:
Result = IMSL_SP_MVMUL(N_Rows, N_Cols, N_Lca, N_Uca, A, X [, SYMMETRIC=value])
Return Value
A one-dimensional array containing the product Ax = b.
Arguments
N_Rows
Number of rows in the matrix a.
N_Cols
Number of columns in the matrix a.
N_Lca
Number of lower codiagonals in a. nuca should be used if a is stored in band format.
N_Uca
Number of upper codiagonals in a. nlca should be used if a is stored in band format.
A
If in coordinate format, a sparse matrix stored as an array of structures. If banded, an array of size (N_Lca + N_Uca + 1) x nrows containing the nrows x ncols banded coefficient matrix in band storage mode. If banded, and the keyword SYMMETRIC is set, an array of size (N_Lca + 1) x nrows containing the nrows x ncols banded coefficient matrix in band symmetric storage mode A(i,j). See Band Storage Format for a description of band storage mode.
X
One-dimensional matrix containing the vector to be multiplied by A.
Keywords
SYMMETRIC (optional)
If present and nonzero, then a is stored in symmetric mode. If A is in coordinate format, then Ax + ATx – diag(A) is returned. If A is banded, then it must be in band symmetric storage mode. See Band Storage Format for a description of band storage modes.
Version History
See Also
IMSL_SP_BDPDFAC, IMSL_SP_BDPDSOL, IMSL_SP_BDSOL, IMSL_SP_CG, IMSL_SP_GMRES, IMSL_SP_LUFAC, IMSL_SP_LUSOL, IMSL_SP_PDFAC, IMSL_SP_PDSOL