Profiles are line plots in which you extract pixels from an image that can be compared to spectral libraries or other pixels.
Click a link below to see details about tools that use a plot.
Spectral Profile (Z profile)
The Spectral Profile plots the spectrum of all bands for the selected pixel. You can extract spectra from any multispectral dataset. ENVI uses header information to scale the plot.
If multiple layers are displayed in the view, ENVI plots a Spectral Profile from each layer. To turn off the plot for an individual layer, disable the check box for that layer in the Layer Manager.
To open a Spectral Profile:
-
Use one of the following:
- Click the Spectral Profile button
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
- Select Display > Profiles > Spectral from the menu bar.
- Right click the image in the Layer Manager and select Profiles > Spectral.
The Spectral Profile window appears, plotting the curve of the center pixel in the view.
-
To plot different spectra:
- Click on a different pixel in the view.
- Click and drag the cursor in the view to browse the spectra under the cursor.
- Import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window. See Import Plot Data for details.
-
To collect and plot multiple spectra:
- Press and hold the Shift key as you click pixels in the view.
- Press and hold the Shift key as you drag the cursor in the view. Each pixel you collect in the view will be marked in a transparent color that corresponds to the plot key.
Note: X/Y pixel coordinates in ENVI-displayed spectra are one less than those displayed in an ENVI Classic Z profile. For example, a pixel location of [X:165, Y:73] in ENVI yields the same spectrum as location [X:166, Y:74] in ENVI Classic.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
Horizontal and Vertical Profiles (X and Y profiles)
The Horizontal Profile plots pixels that fall along the horizontal cursor line (column). The Vertical Profile plots pixels that fall along the vertical cursor line (row).
For color composite images, the profile is plotted for all three images in their corresponding colors (R,G,B). For single-band images, the profile of that band is plotted in red.
To open a Horizontal or Vertical Profile:
-
Use one of the following:
- Select Display > Profiles > Horizontal or Display > Profiles > Vertical from the menu bar.
- Right click the image in the Layer Manager and select Profiles > Horizontal or Profiles > Vertical.
Depending on your selection, the Horizontal Profile or Vertical Profile window appears, plotting the curve of the center pixel in the view. A red line in the view indicates the column or row of pixels that are associated with the pixel that is selected.
-
To plot different columns or rows:
- Click on a different pixel in the view.
- Click and drag the cursor in the view to browse the spectra under the cursor.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
Arbitrary Profile (Transect)
The Arbitrary Profile plots the pixels of an image that lie beneath a transect.
To open an Arbitrary Profile:
-
Use one of the following:
- Click the Arbitrary Profile (Transect) button
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
- Select Display > Profiles > Arbitrary from the menu bar.
- Right click the image in the Layer Manager and select Profiles > Arbitrary.
The Arbitrary Profile (Transect) button is enabled on the toolbar.
- Perform one of the following actions to define the new transect:
In the view, click to mark the vertices of the transect, or click and drag to draw a line. Data for the pixels under the transect will be included in the plot. To complete the line, press the Enter key twice, or right-click and select Complete and Accept Polyline. The Arbitrary Plot window appears.
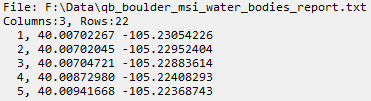
To create the transect from ASCII data, right-click in the view and select Import from ASCII. Select an ASCII text file (.txt) or CSV file (.csv) with the records you want to import, and click Open. The Import from ASCII dialog appears. The File Preview section shows the columns of data that were imported; for example:
In the X field of Data Columns, select the column number that contains longitudes or eastings. In the Y field of Data Columns, select the column number that contains latitudes or northings. Using the example above, the X field is column #3 since that column contains longitudes. The Y field is column #2 since that column contains latitudes:
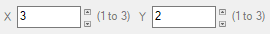
Select the Coordinate System of the imported ASCII data. See Select Coordinate Systems for further instructions. The default is Geographic Lat/Lon WGS-84. Then click OK. The transect is displayed in the view, and the Arbitrary Plot window appears.
To create the transect from an existing vector record, right-click in the view and select Import from Vector. The Import from Vector dialog appears. Select a shapefile (.shp) or ENVI Vector File (.evf). In the Record ID field, indicate the specific record number you want to use for the transect. Then click OK. The vector record is displayed in the view. Right-click inside the vector record and select Accept. The Arbitrary Plot window appears.
- You can repeat this process to collect data for multiple transects.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
ENVI Plot Window
The ENVI Plot window is useful when you want to collect spectra from various sources and compare them in one window.
To open an ENVI Plot window:
-
Use one of the following:
- Select Display > New Plot Window from the menu bar to open an empty ENVI Plot window.
- In any profile window, select Options > New Window with Plots to copy the curve in that profile window into an ENVI Plot window.
The ENVI Plot window appears.
-
Add spectra as follows:
- From any profile window, drag and drop a spectrum plot key from the profile window to the ENVI Plot window. The Scale Incoming Curve dialog appears for you to provide wavelength units and/or Y-scale factor information for the incoming curve.
Explained Variance Plot
The Explained Variance appears during certain ENVI workflow steps. The plot shows the sorted eigenvalue (or spatial coherence) contribution percentage of each band after image transform has been performed.
Use the plot as a guidance for choosing the number of bands to keep for workflow processing.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
Series Profile
The Series Profile plots the pixels within a specified band of a spatiotemporal series file (.series). All files that make up the series must occupy the same geographic area and must possess regular bands and a regular grid. Profiles are drawn based on an equally spaced sampling of the series, with a default maximum index size of 100 data sets. This value can be modified with the Series Profile Maximum Index Size preference.
Tip: To ensure that a series file meets the requirements for creating a Series Profile, right-click on the series layer in the Layer Manager and select View Metadata. The Regular Grid and Regular Bands preferences should be set to true.
To open a Series Profile plot:
-
Open and display a (.series) file.
- Use one of the following:
- Select Display > Profiles > Series from the menu bar.
- Right click the series entry in the Layer Manager and select Profiles > Series.
- In the Series Manager dialog, Series Profile from the drop-down menu
 .
.
-
To plot different bands, click the Source drop-down list in the profile window. The plot title will display the selected band.
-
To plot multiple pixels, press and hold the Shift key as you click pixels in the view.
- To toggle the X-axis label on series files containing time data, click on the X: drop-down list and choose between Time and Series Index. Series files without time data will display only the Series Index option.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
Spectral Collection Plot
The Spectral Collection Plot plots data values for spectra collected during Spectral Collection Classification.
To open a Spectral Collection Plot:
-
With endmember spectra imported into the Spectral Collection Classification dialog, use one of the following:
- Select one or more spectra to plot and click the Plot Spectra button
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
- Right-click on the Endmembers folder and select Plot Spectra to plot all imported spectra.
- Right click on an individual spectra under the Endmembers folder and select Plot Spectra to plot that spectrum.
The Spectral Collection Plot window appears.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
Temporal Profile
The Temporal Profile plots data values for all bands to show how the selected pixel has changed over time.
To open a Temporal Profile:
-
With a temporal cube file open, use one of the following:
- Click the Spectral Profile button
 on the toolbar.
on the toolbar.
- Select Display > Profiles > Spectral from the menu bar.
- Right click the image in the Layer Manager and select Profiles > Spectral.
The Temporal Profile window appears, plotting the curve of the center pixel in the view.
-
To plot different pixels:
- Click on a different pixel in the view.
- Click and drag the cursor in the view to browse the changes over time under the cursor.
-
To collect and plot multiple pixels:
- Press and hold the Shift key as you click pixels in the view.
- Press and hold the Shift key as you drag the cursor in the view. Each pixel you collect in the view will be marked in a transparent color that corresponds to the plot key.
Here are links to additional details:
-
You can import data from an ASCII file or spectral library using the Import drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The plot window controls and plot properties change the display and appearance of the plot.
- You can export data using the Export drop-down list in the profile window.
-
The Material Identification Tool can be used with a profile or plot to compare an unknown spectrum with a spectral library of known spectra and rank the similarity between the two using a variety of common spectral similarity algorithms.
Statistics View
The Statistics View plot shows basic statistics (minimum, maximum, mean, and standard deviation) for each band. See Statistics for details on how to compute statistics and display them in the Statistics View using different ENVI tools.
Drag and Drop Curves to Other Profiles or Plots
You can drag and drop curves between the Spectral Library Viewer and any profile or ENVI Plot window for analysis:
- Open a spectral library file in the Spectral Library Viewer.
- Click the arrow on the right side of the profile window and the Spectral Library Viewer to expand the panels and show the plot key.
- In the profile window, select a curve from the plot key. You can use Ctrl+click to multi select.
- Drag the selected curves to the Spectral Library Viewer. The curves appear in the Spectral Library Viewer plot. If the incoming curve or the receiving plot (or both) are missing wavelength units and/or y-scale factor information, the Scale Incoming Curve Data dialog appears.
See Also
Plot Window Controls, Plot Properties